* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
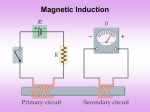
Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday’s Law 20.10 Applications: Motors An electric motor takes advantage of the torque on a current loop, to change electrical energy to mechanical energy. 20.10 Applications: Motors • • • • • • There are 2 types of motors: DC & AC When a current is passed through a wire loop (armature) in a magnetic field, there is a magnetic force on armature, which makes a 180o turn In order to make 360o rotation, split-ring commutator (attached to armature) allows current to change direction in armature (due to contact with brushes) A change in direction of current means magnetic force in opposite direction and thus a further 180o turn When current supplied to commutator is AC, commutator has two separate parts (slip ring commutator), each connected to one end of armature Thus there is a reversal of current supplied by voltage source (no need for split-ring commutator) Use 3rd Right Hand Rule for determining direction of Fm DC Motor Split-ring commutator 20.10 Applications: Motors AC Motor Slip-ring commutator 21.1 Induced EMF Note: EMF or Electromotive Force (Ɛ) is actually a voltage produced by a battery or magnetic field Faraday observed that a steady current in X produced no current in Y. When the current was starting or stopping in X, current was produced in Y. He concluded only a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current. This is called an induced current. 21.2 Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law The induced emf in a wire loop is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux (Ф) through the loop. 21.2 Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law The magnetic flux proportional to the total number of lines passing through the loop. 21.2 Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law Faraday’s law of induction: [N loops] If the magnetic flux through a coil(s) of wire changes with time, an emf is induced in the coil(s). The magnitude of the induced emf equals the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the loop times the number of loops, N, in the coil. 21.2 Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law The minus sign gives the direction of the induced emf: An induced emf always gives rise to a current whose magnetic field opposes the original change in flux (Lenz’s Law). Lenz’s Law is the ‘electromagnetic’ version of the Law of Conservation of Energy In (a) the magnetic field and flux are increasing. The current moves in the direction to oppose that – to decrease the magnetic field. In (b) the magnetic field and flux are decreasing. Again, the current moves in the direction to oppose that. In (c) there is no change in flux, so there is no induced emf. Induced EMF Therefore, a changing magnetic field induces an emf. (Faraday’s experiment used a magnetic field that was changing because the current producing it was changing; the previous graphic shows a magnetic field that is changing because the magnet is moving.) 21.2 Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law Magnetic flux will change if the area of the loop changes: Current increases in the direction shown (clockwise) to maintain original flux. 21.2 Faraday’s Law of Induction; Lenz’s Law Magnetic flux will change if the angle between the loop and the field changes: Flux is decreasing so the current will go in the clockwise direction to increase flux. 21.5 Electric Generators A generator is the opposite of a motor – it transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy. This is an AC generator: The axle is rotated by an external force such as falling water or steam. The brushes are in constant electrical contact with the slip rings. 21.5 Electric Generators • • • • • • • • There are 2 types of generators: AC & DC A wire loop rotated in MF by external means (i.e. crank) As loop rotates, motion of wire loop changes in the magnetic field and thus an induced current is produced The end of loop connected to slipring commutator Connections to external circuit made by stationary brushes in contact with commutator When loop is 1/2 way through rotation in MF, the current flows one direction When completing other 1/2 rotation, the current flows in opposite direction producing alternating current (AC) For direct current (DC) generation, split-ring commutator used to produce pulsating (or rectified) direct current AC Generator 21.5 Electric Generators DC Generator 21.7 Transformers and Transmission of Power A transformer is a device that changes the magnitude of an AC voltage using EM induction. This is a step-up transformer – the emf in the secondary coil is larger than the emf in the primary: 21.7 Transformers and Transmission of Power • • • • • Transformers consist of 2 coils of wire wound around a core of soft iron The coil connected to input AC voltage source (primary) has N1 turns The 2nd coil connected to a resistor (secondary) has N2 turns If N2 > N1, then V2 > V1 step-up transformer If N2 < N1, then V2 < V1 step-down transformer 21.7 Transformers and Transmission of Power Transformers work only if the current is changing; this is one reason why electricity is transmitted as ac.