* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Subject - Notekhata
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
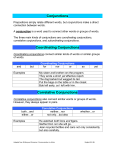
Presented By Md. Habibul Islam Hamdu Deprtment Of Marketing Hamdard University Bangladesh What is a sentence? A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. Ex. This gift is for you. Every sentence has two parts: Subject Predicate Subject The subject tells who or what the sentence is about. Complete subject: My tutors are outstanding. Simple subject: Yvette is a tutor. Predicate Complete predicate: words that tell what the subject is or does Verb: the key word of the complete predicate – also known as simple predicate Ex. The girl runs real fast. Noun Computer Table A noun is the name of a person, a place, a thing, or an idea. Kinds of Nouns Proper Noun Mark Common Noun sun Abstract Noun love Collective Noun class Plural Forms of Nouns Regular Plural Nouns Irregular Plural Nouns Bus -------buses Student- students Leaf ------leaves Child----- children Woman-- women City ------ cities Pronouns A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun. Kinds of Pronouns Subject Relative Object Interrogative Possessive Demonstrative Reflexive Intensive Kinds of Pronouns Subject I You He She It We You They Object Me You Him Her It Us You Them Possessive Possessive Adjectives Pronouns My Your His Hers It Our Your Their Mine Yours His Hers Its Ours Yours Theirs Kinds of Pronouns Reflexive Relative Interrogative Demonstrative Myself That Who This Yourself Which Whose That Himself Who What These Herself Whom Whom Those Itself Whose Which Ourselves Yourselves Themselves Kinds of Pronouns Indefinite All Anyone Either Few Much No one Some Such Another Anything Everybody Many Neither One Somebody Any Both Everyone More Nobody Other Someone Anybody Each Everything Most None Several Something Kinds of Verbs Action - Ex. Dive Linking - Ex. Am Helping or auxiliary Ex. have, do, be Verb Tenses Present Past Future Present Progressive Past Progressive Future Progressive Present Perfect Past Perfect Future Perfect Adjective An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. Answers the questions: What kind? I like the long, green rectangle. Which one? I want that dress. How many? I see twelve circles. Adverb A word that modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Answers the questions: When? I will see you tomorrow. Where? The dog is outside. How? She worked happily. To what extent or degree? They swam deeper into the ocean. In what manner? Mary sang beautifully. Prepositions A word that shows a relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other words in the sentence. Example: The students of this university are dynamic. List of Prepositions Along Among Around As At Before Behind Below Beneath Beside Besides Between Beyond By Despite Down Except For From In Near More Prepositions Of Off On Onto Out Outside Over Past Since Through Till To Toward Under Underneath Until Up Upon With Within Without Compound Prepositions According to As of As well as Aside from Because of By means of In addition to In front of In place of In regard to In respect to In spite of Instead of On account of Out of Prior to Conjunction A conjunction is used to join words or group of words Kinds of conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions Correlative conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions Conjunctive Adverbs Coordinating Conjunctions A coordinating conjunction connects individual words or groups of words that perform the same function. Ex. I dance and sing. And But Or Nor For Yet Correlative Conjunctions A correlative conjunction consists of two or more words that function together. Ex. Either Bill or Mary wrote the poem. Either...or Neither…nor Whether…or Not only…but (also) both…and Subordinating Conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions introduce subordinate clauses, which are clauses that cannot stand by themselves as a complete thought. The subordinate conjunction connects a subordinate clause to an independent clause, which can stand by itself. Ex. We will go whale watching if we have time. List of Subordinating Conjunctions Time After As As long as As soon as Before Time Since Until When Whenever While Purpose In order that So that That List of Subordinating Conjunctions Manner Cause As As if As though Because Comparison As Tha n Subordinating Conjunctions of Condition Although Even though Though As long as If Unless Even if Provided that While Conjunctive Adverbs A conjunctive adverb is an adverb that functions somewhat like a coordinating conjunction. Conjunctive adverbs usually connect independent clauses. Conjunctive Adverbs A semicolon precedes the conjunctive adverb, and a comma usually follows it. Ex. I have to clean my room; therefore, I can’t go to the movies with you. List of Conjunctive Adverbs Accordingly Also Besides Consequently Finally Furthermore However Indeed Instead Later Moreover Nevertheless Otherwise Still Therefore Thus Interjection An interjection is a word that expresses strong feelings It is followed by an exclamation mark (!) List of Common Interjections Really! Whoops! Good grief! Honestly! Good! Oh! What! Well! Sh! Ugh! Alas! Yes! Ahem! My! Please! No! Unbelievable! Congratulations! My goodness! Acknowledgments Faculty Enrichment and Educational Technology Center Zobeida Rosado LAD GRAMMAR WORKSHOP Prepared by Professors Delia Serrano and Jennifer Soler University of the Sacred Heart Department of Humanities copyright © August 2002