* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 - Ms. De masi Teaching website
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Bulgarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Danish grammar wikipedia , lookup
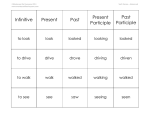
The present perfect expresses an action or state that is completed at some indefinite past time, but which still applies in the present. The present perfect tense consists of has or have + the past participle. › Example: The Queen has visited Canada many times. The past perfect expresses some action or state that was completed before some other past action. › Example: We had already eaten when we arrived at the hotel. Progressive tenses indicate a continuing action or state. The present progressive shows that an action began in the past and is now continuing in the present. The past progressive indicates an action that was in progress at some point in the future, or an action that will occur at a particular time in the future. Progressive tenses are formed by using the verb be plus the present participle. The present participle is the form of the verb that ends in –ing. › Examples: Present Progressive: (is/are + present participle) My head is pounding. Past Progressive: (was/were + present participle) A fly was buzzing all night. Future Progressive: (will be + present participle) We will be arriving on Tuesday. Write a sentence for each of the following verbs and tenses 1. Fall (present progressive) 2. Discuss (past progressive) 3. Prepare (future progressive) Use may to ask for permission. Use can to express the ability to do something. › Examples: May I build a skateboard ramp in the backward. Errol can do amazing tricks Teach means “to give instruction.” Learn means “to acquire knowledge.” › Examples: Mme. Lefarge teaches us French. When will you learn to accept people for who they are? Sit means “to take a resting position.” Its principal parts are sit, sat. Set means “to place.” Its principal part is set. › Examples: Sit down and rest. She set the vase on the table and left the room. Lie means “to recline” or “to occupy a certain space.” Its principal parts are lie, lay, lain. The present participle is laying. Lay means “to place.” Its principal parts are lay, laid. The present participle is laying. › Examples: He lay down on the bed for a brief rest. She laid the sleeping baby in the crib. A verbal is a verb form that cannot function on its own as a verb. Three forms of verbals are participles, gerunds, and infinitives. The past participle and present participle can be used on their own as adjectives. › Examples: Past Participle: burnt toast, frozen tuna Present Participle: a laughing smile, a running jump. A gerund is a present participle that is used as a noun in a sentence. › Examples: Running is hard on your knees. Irwin enjoys baking. The infinitive is the basic form of the verb, which is often preceded by to. Examples: To help, to feel, to arrive The infinitive can be used as an adjective, an adverb, or a noun. Examples: His will to live was very strong. (adjective) He was lucky to survive. (adverb) To err is human. (noun) •A verb must agree in number with its subject. Examples: The dog is barking. The cats are hissing. •Difficulties with subject-verb agreement arise in the following instances. Situation Rule Example (Subject/verb) Collective noun as the subject Usually, use with a singular verb. The jury was out for three days. Indefinite noun as the subject Usually, use a singular verb, except with both, many, few, others, and several, which take a plural. Everyone is happy for you. One of the players is hurt. Compound subjects connected by and Usually, use a plural verb, unless the items form a single unit, or refer to the same person or thing. Harry and Manny are knocking down a wall. The soup and sandwich is on sale today. (single unit) My oldest friend and best buddy has moved away. (refer to the same person) Compound subjects connected by or or nor Make the verb agree with the part closest to it. Either your job performance or your marks are going to suffer. Either your job performance is going to suffer. Some of the cake is left over. Some of the houses are sold. When words seperate the subject and the verb in a sentence, be sure to make the verb agree with the true subject. › Example: A pair of gloves was left in the snow. (subject is pair, not gloves) In sentences that begin with There is or There are, the verb agrees with the subject that comes after the verb, not with there. Complete the sentences below. Use a verb in the present tense that agrees with the subject. 1. The Singer family and I_______________ 2. The school band___________ 3. Neither the kittens nor their mother_____ Voice refers to the relation of a subject tot he action expressed by the verb. In the active voice, the subject does the action. › Example: The passengers tackled the hijacker. In the passive voice, the subject is acted upon. Form the passive voice by using a form of be (e.g., is, was, has been, will be) plus the past participle. › Example: The hijacker was tackled by the passengers. Use the passive voice when the doer of the action is unknown., unimportant, or obvious. In most other cases, use the active voice. › Examples: A man was robbed near here last night. (unknown actor) The solution was heated to 130 °C. (unimportant actor) The defendant was found guilty of murder. (obvious actor) Rewrite each sentence in the active voice. 1. Each of the tales in told by a different character. 2. Many writers have been influenced by Chaucer’s bawdy humour and insightful characterizations. A pronoun is a word that replaces or stands for a noun or another pronoun. Some common pronouns include the following: I it Me He She We They Them Himself Herself This That those Any some everyone who what The word that a pronoun replaces or refers back to is called its antecedent. Pronouns must agree with their antecedents in number and, in some cases, in gender. › Example: antecedent pronoun My mother thought that she had forgotten the car keys. When one of the singular indefinite pronouns listed below is used as the antecedent to a pronoun, the pronoun must be singular. Everyone Everybody Someone Somebody Anyone Anybody No one Nobody each either neither nothing In everyday conversation, the plural pronouns they, them, or their are often used to replace a singular indefinite pronoun. However, this is not acceptable in formal writing. Instead, use his or her, or change the subject to make it plural. Examples: Incorrect: Everyone is responsible for their own belongings. Correct: Everyone is responsible for his or her own belongings. Correct: Passengers are responsible for their own belongings.