* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Bound variable pronoun wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
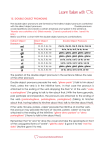
Direct Objects & Direct Object Pronouns Direct Objects & Direct Object Pronouns Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. Rafaela pone la mesa. Rafaela sets the table. Siempre pido la sopa. I always order the soup. Direct Objects & Direct Object Pronouns A direct object can be a noun or a pronoun. Recall that a pronoun takes the place of a noun. Use direct object pronouns to avoid repeating nouns that have already been mentioned. These pronouns must agree with the nouns they stand for. Direct Objects & Direct Object Pronouns Masculine Feminine Singular lo him, it la her, it Plural los them las them Direct Objects & Direct Object Pronouns Direct object pronouns go before the conjugated verb. If there is an infinitive (a verb before its conjugated) in the sentence, the pronouns can go before the conjugated verb or they can be attached to the end of the infinitive. No DOP ¿Quién va a pedir el flan? ¿Quién prepara los sándwiches? ¿Quién va a preparar la cena? DOP Yo lo voy a pedir Yo los preparo. Mi padre la va a preparar. OR Mi padre va a prepararla. What are the four direct object pronouns? Why do you use direct object pronouns? Write the sentence below then underline the direct object. Yo como las hamburguesas. Using that same sentence, rewrite it using the correct direct object pronoun. Be sure to place the direct object in the correct location. Activity 26: Answer the question using the correct direct object pronoun. Activity 27: Say who is going to the bring the following items to the party. Give a question and then the answer using a direct object pronoun in the response. Activity 28: Who is responsible for the following chores in your house? Use the correct direct object pronoun in your answers.