* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Windows Forensics - University of Washington
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Windows Phone 8.1 wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
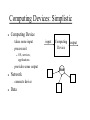
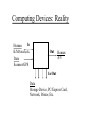
Windows Forensics 24 Jan 2008 TCSS431: Network Security Stephen Rondeau Institute of Technology Lab Administrator Agenda Forensics Background Operating Systems Review Select Windows Features Vectors and Payloads Forensics Process Forensics Tools Demonstration Forensics Background Inspection of computer system for evidence of: crime unauthorized use Evidence gathering/preservation techniques for admissibility in court of law Consideration of suspect's level of expertise Avoidance of data destruction or compromise Operating System Review What does an OS do? Operating System Review What does an OS do? starts itself low-level management of: higher-level management of: interrupts, time, memory, processes, devices (storage, communication, keyboard, display, etc.) file system, users, user interface, apps addresses issues of fairness, efficiency, data protection/access, workload balancing Select Windows Features Kernel vs. User Mode Kernel features (architecture) device drivers installable file system object security Services User accounts, passwords and privileged groups Security policies Computing Devices: Simplistic Computing Device takes some input processes it provides some output connects device Data Computing Device OS, services, applications Network input Hub output Computing Devices: Reality In Human K/M/touch,etc. Data Scanner/GPS Out Human A/V In/Out Data Storage Device, PC/Express Card, Network, Printer, Etc. Computing Devices: Connections removable media PC/Express Card wired floppy,CD/DVD,flash,microdrive serial/parallel,USB,Firewire,IDE/SATA,SCSI/SAS twisted pair wireless radio (802.11, cellular, Bluetooth) Infrared (IR) Ultrasound Vectors and Payloads Vector: route used to gain entry to computer via a device without human intervention via an unsuspecting or willing person's actions Payload: what is delivered via the vector malicious code may be multiple payloads spyware, rootkits, keystroke loggers, bots, illegal software, spamming, etc. Forensics Process Assess (after permission is granted) Acquire determine how to approach affected system(s) inspect physical environment watch out for anti-forensics, booby-traps consider how to stop computer processing capture volatile data copy hard drive Analyze Volatile Data All of RAM, plus paging area Logged on users Processes (regular and services) Process memory Buffers Clipboard Network Information (incoming and outgoing) Command history Nonvolatile Data Partitions Files hidden, streams Registry Keys Recycle Bin Scheduled Tasks User Account and Group Information Logs What to Look For Know baseline system: what to expect of good system Malware Footprint in logs on file system (changed dates/sizes, hidden) in registry in startup areas in services list in network connections Abnormality: function, performance, traffic patterns Cross-check with multiple tools Microsoft Tools Basic Network tools netstat -anob, nbtstat, ping, tracert, arp, netsh, ipconfig dir /ah, dir /od, dir /tc, findstr, cacls File Services Prevent: Windows Update, Time Service, Routing and Remote Access, LocalService, NetworkService, Runas Inspect: net user/group/localgroup, Active Directory Users and Groups, Event Viewer, EventCombMT, systeminfo, auditpol, Security Configuration Manager Fix: Malicious Software Removal, Security Configuration Manager net start/stop, sc, services.msc Process: tasklist, taskkill, schtasks External Tools www.sysinternals.com variety of Windows tools to monitor and analyze www.e-fense.com: Helix Windows tools Windows Forensics Toolkit™ trusted commands RAM/disk imaging, password recovery tools some www.sysinternals.com tools bootable to Knoppix with many file system tools www.rootkit.com Advice For your systems: Prevent: Analyze: update, monitor, block, isolate, backup find vectors and payloads Recover: off-network restore, re-install or re-image block vectors and/or payload effects before going onnetwork References Windows Forensics and Incident Recovery, Harlan Carvey, Addison-Wesley 2005 Windows Forensic Analysis DVD Toolkit , Harlan Carvey, Syngress 2007 File System Forensic Analysis,Brian Carrier, Addison-Wesley 2005 Rootkits, Greg Hoglund and James Butler, Addison-Wesley 2006