* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
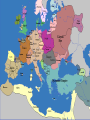
Download Medieval Kingdoms in Europe
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Pomerania during the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
England in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Scotland in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Feudalism in the Holy Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
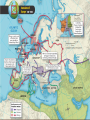
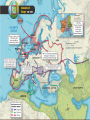
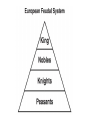
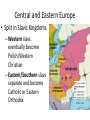
Medieval Kingdoms in Europe Ch 4, p. 61 Medieval Europe Chaos ensues… Ch 4.1 Vocab • • • • • • • • Feudalism Vassal Knight Fief Feudal contract Chivalry Enabled Contract Fall of Carolingian Empire • Centralized Gov’t. falls apart b/c: –Divisions after Charlemagne’s death –Viking invasions Death of Charlemagne • Carolingian Empire divided into 3 territories – Fought over by Charlemagne’s grandsons • Vikings attack! – Excellent shipbuilders/sailors – Strong warriors, BERZERKer mode • Local nobles gained power throughout the various conflicts Vikings…sorta trendy http://www.youtube.com/v/oKiYuIsPxYk Development of Feudalism • Pops up b/c: –Inability of rulers to defend subjects –Vassalage and knighthood –Feudal contracts Feudal Society! • New social & political system – Lords control large territories instead of gov’t. • Land offered in exchange for sworn allegiance and other obligations • Vassals and knights provided military service to their lords. • On any other continent this would be known as a ‘Warring States’ period or Civil War. Feudalism • Warfare conducted with localized militias • Chivalry critical • Aristocratic women – Could not hold property, BUT remained in control of house, accounts, and a large group of servants. Eleanor of Aquitaine Structure of Fuedalism • Local lords were chief political, social, and economic authorities – Warriors (incl. knights) were required to pledge loyalty • In return, warriors received land, food and safety • Multiple landholders ruling the land…instead of a centralized gov’t. Think-Pair-Share! • How did the introduction of larger horses lead to the use of heavily armored knights? OR • What were some of the ideals of chivalry? Ch 4.1 Discussion & Review • The Medieval European relationship btwn lords and vassals is called… – Feudalism • Describe the traits of a chivalrous knight. – courtesy, fairness, piety, & devotion to honor • Why was feudalism developed? – Loss of centralized power Peasants, Trade & Cities! Ch 4.2, p. 68 Feudal Society • What kind of protection would lords be able to offer to peasants? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q V7CanyzhZg&feature=plcp Ch 4.2 Vocab • • • • • Carruca Manor Serf Bourgeoisie Patrician New Agriculture • Allows explosion in population growth –Relative peacefulness –Good climate –New Farming methods Agriculture Post-1000AD • New methods = population growth – Wind and water tech, reducing human/animal labor – Carruca • Heavy ox-drawn, wheeled plow w/ iron plowshare –Allowed turning of heavier soil and large-scale coop farming – Increased efficiency in land use • Three-field system instead of two-field Manorial System • Manors – An estate owned by a lord and farmed by peasants, most of whom were serfs • Peasants (own land) – Lived in simple cottages and raised food/made goods for themselves/lords • Serfs (indentured servants) – Work land 4 nobles • Paid rent • Subject to nobles’ control Query • In what way was manorialism an economic system? – Exchange of goods and services • Lord provides land & protection • Peasants provide labor and share of crops Growth of Trade • Money and rise of capitalism! – Economy based on gold and silver, rather than barter – Investment for profit begins • Centers of trade – Venice & the Mediterranean: cloth, swords, silks, sugar & spice – Flanders: wool, furs, tins, hemp, honey • Hanseatic League – >100 cities in the Baltic Sea and North Sea areas banded together for mutual protection/trade Growth of Trade • • • • Revival of trade routes Revitalization and growth of cities Expansion of merchant & artisan classes Increase in manufacturing & consumption of goods • Increase in TAXES, money & banking Urbanization • Revival of old Roman cities • Freedom from Lords – Buy land with trade • Conditions – Walls, unsanitary, lots of men • Industry/guilds – Manufacturing led to organized labor Guild House in Stormwind, WoW Townsppl Gain Power • Ruling class sell liberties to ppl who could pay • Unique laws – Right to buy/sell prop. – Freedom from military service to lord – Personal freedom – Escaped serfs who lived in the town received freedom for year and one day WoW Dance Party Think-Pair-Share • What events during the Middle Ages led to a growth of cities? OR • How did new farming methods benefit Europe in the Middle Ages? Major Changes in Europe • • • • Growth in population Stability achieved by manorial system Revival of trade Explosion of cities some become very strong Town Charters • Disparity in power btwn state and towns – Nobles decide to grant charters to keep towns under control • Some last for hundreds of years Ch 4.2 Discussion & Review • What is the vocab word for a heavy wheeled plow w/ an iron plowshare? – Carruca • What was a long term result of ppl living in walled cities? – Basic freedoms for sale • How did the Hanseatic League benefit Northern Europe? – Protecting trade and promoting economic dev. Growth of Euro Kingdoms aka prepare for a random assortment of cultures from the Middle Ages Ch 4.3, p. 73 Ch 4.3 Vocab • • • • Common law Magna Carta Parliament Estate England in High Middle Ages 1000-1300 • William of Normandy defeats English –Battle of Hastings –Becomes KING • Lands to Norman knights, makes everyone swear loyalty • Adopts existing Anglo-Saxon institutions –Merging of French and Anglo languages creates new English language Norman Conquest of England • New Anglo-Saxon culture – Nobles had to swear loyalty to William as sole ruler of England – Norman knights given fiefs – Current-day institutions made by Normans: • Sheriff’s office • System of taxation • Royal courts – Ruling class spoke French Henry II and John • Henry II – Increased the power of the monarchy • Expanding control of courts – But not able to suppress the power of the Church • King John – Seals the Magna Carta • Recognizing the rights of nobles, monarchy limited –Eventually leads to a Parliament under reign of Edward I http://www.youtube.com/v/H3r9bOkY W9s Development of English Law & Gov’t. France in High Middle Ages • Philip II Augustus – Regains control from England • Louis IX – Super religious, into justice • Philip IV – Expanded gov’t., created French parliament • Estates-General French Fashion • Groovy link on French Fashion through the ages: – http://www.etsy.com/listing/83625151/fashionhistory-folk-clothes-antiquity Query • Contrast English/French rulers with the German rulers of the High Middle Ages. – English and French kings strengthened their monarchies by expanding territories AND controlling nobles….(Magna Carta) • BUT German emperors dropped the ball with nobles Holy Roman Empire • Otto I, a German king, creates the Holy Roman Empire – Pope names Otto emperor of the Romans, AD 962 • In exchange for Otto’s protection of the church Holy Roman Empire • Later, in Italy – Emperors Fredrick I and Fredrick II wanted to expand into Italy for land/revenue • Creates power vacuum back home in Germany –German nobles build small German states…. • Holy Roman Empire fails to control Germany or Italy. Central and Eastern Europe • Split in Slavic Kingdoms – Western slavs eventually become Polish/Western Christian – Eastern/Southern slavs separate and become Catholic or Eastern Orthodox Think-Pair-Share • Why do you think the various Slavic kingdoms split religiously? Mongols Attack! • Overrun Russia in 1200s • Prince Alexander Nevsky defends Russia, for Mongols vs. Germans – Mongol khan rewards Nevsky with title ‘Grand Prince’ – His descendants become leaders of Russia Sign of the Order of Saint Nevsky Monument in Saint Petersburg • Also: – Movies – Books – Graphic Novel – Soviet Propaganda Ch 4.3 Discussion & Review • What was the charter that codified the rights of Kings and vassals? – Magna Carta • T/F: a parliament is a representative gov’t. – True…in that nobles have their opinions represented • The Holy Roman Empire stemmed from which European state? – Germany