* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Middle Ages Study Guide KEY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
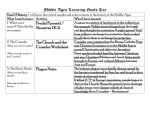
World History Honors Unit 6: Middle Ages Name: KEY Test Study Guide Part I: Define the following terms/events and explain the significance for greater understanding. 1. Feudalism: Political system of local government based on the granting of land in return for loyalty, military assistance and other services 2. Manorialism: Economic System; the Lord’s self-sufficient farming estates where lords and peasants shared land 3. Fief: land granted by a lord or landowner in exchange for military protection and other services. 4. Chivalry: A code of behavior for knights in medieval Europe, stressing ideals such as courage, loyalty and devotion 5. Great Schism: a division in the medieval Catholic Church during which rival popes were established in Avignon and in Rome. 6. Crusader: knights who went to the Holy Land in hopes of winning control 7. Lay Investiture: the appointment of religious officials by kings or nobles 8. Parliament: a body of representatives that makes laws for a nation created as a result of the Magna Carta in order to check the power of the King. 9. Tithe: Church tax, typically 1/10th of a church member’s income given to the church every year. Part II: Explain the following people including their significance and contributions. 10. Charlemagne: “Charles the Great”, united the kingdoms of Europe under one leader; he fought Muslims in Spain and tribes through out Germanic lands; he spread Christianity through his conquests. He was crowned the “Roman Emperor” by Pope Leo III. 11. Pope Urban II: Leader of the Catholic Christian church, he issued a call for what he termed a “holy war” to gain control of the holy land. 12. Saladin: Muslim leader from 1100s; fought against the Christians in the crusades for the Holy Land of Jerusalem 13. Richard the Lionhearted: English king who led crusades against Saladin and Muslims 14. William the Conqueror: the duke of Normandy; invaded Britain with the goal of conquering land. He claimed the English crown. 15. Joan of Arc: French peasant girl who felt moved by God to rescue France from its English conquerors. She led the French army in battle against an English fort that blocked important roads. She was later condemned as a witch and a heretic because she claimed she heard voices. She was burned at the stake. Part III: FULLY complete the following questions including all relevant information and answering all parts of the question. 16. How do invasions lead to the fall of Rome and the rise of Feudalism in Europe? Because the invasions and warfare were common, trade was disrupted, cities were left abandoned, and the populations shifted to more rural areas for safety. This led to the decline of learning, a loss of common languages because there was little communication in rural areas . 17. What is the Norman Conquest and how does it change England (give multiple reasons!)? Invasions by Norman leaders (descendents of the Vikings) from Normandy. Normans won control of English Land 18. What were some reasons for the Crusades? Wealth, glory & honor, young sons who would not inherit property gained notoriety & wealth, Merchants looked to make money on the trade routes, Religious, zeal, Christians would stop fighting each other and fight collectively against an enemy. 19. What are some effects of the Crusades? Weakened the power of the Church, and nobility, thousands of Crusaders died, stimulated trade between Europe & Asia, intolerance and prejudice left between Muslims & Christians, growth of trade, towns and universities. 20. Who signed the Magna Carta? Who initially benefitted from this document? King John of England; it initially benefitted the rights of nobles in order to limit the king’s power, but eventually guaranteed no taxation without representation, a jury trial and protection of the law. 21. How does the Magna Carta change English government and lead to democracy? Forces the king to create a parliament, which is the representation of the people. This parliament must approve the decisions of the king, giving the people a voice in what happens. 22. Where did the Black Death first enter Europe? How did it get there? Began in Asia and traveled through the trade routes. It arrived in Europe in 1347 through a merchant ship carrying rats and infected goods. 23. How was the Black Death spread? Rats carrying infected fleas; infected garbage & sewer waste infected water sources. 24. What are some effects of the Black Death? (Political, Religious, Economic) Economic-Town populations fell, trade declined, prices rose. Fewer people= high demand for healthy workers; could demand higher wages Religious-loss of faith when prayers and penance did not save bodies; many clergy left and charged high fees for anointment of the sick services. Social- Pessimistic about life, fear of dying, 25. What was the cause of the Hundred Year’s War? War fought over the successor to the French throne (claimed by English king Edward III) 26. What are some results of the Hundred Years’ War? English only claimed the port of Calais; French had terrible loss of lives, property & money; both experienced internal problems 27. How do changes in armor and weaponry affect feudalism? New techniques like armored horsemen helped troops to win battles and the horse became a key status symbol. This also led to the rewarding of knights and expectations of a knight in society (Chivalry). Hierarchy of Feudalism: List titles as well as describe their position in society Title 28. 29. 30. 31. Role and Description King-reigned over the land/technically owned all land Lords/Nobles-granted land by the king/powerful Nobles Knights-mounted warriors who pledged to defend their lords’ land in exchange for fief Peasants/Serfs- tied to the land; could not lawfully leave the place they lived Hierarchy of the Church: List titles as well as describe their position in society Title 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. Role and Description Pope- leader of the church, makes theological decisions, “holds power” over emperors Cardinals-Rule over lower levels, elect popes, form the Curia as papal advisors and court Archbishops-often nobles and had land/wealth, sometimes vassals to church, rule over lower levels Bishops-settle disputes over teachings, supervise priests, administer sacraments Priests-interact daily with commoners, main contact with the church, perform masses, most sacraments