* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PROJECT CLIL
History of metamaterials wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Electronic band structure wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
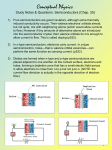
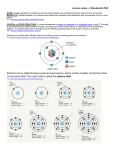
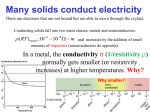
CLIL ELETTRONICA SEMICONDUCTOR INTRODUCTION Some materials conduct eletric charge better than insulators but not as well as conductors. These materials are called SEMICONDUCTORS SEMICONDUCTORS 3 POINTS: 1. STRUCTURE 2. CONDUCTIVITY 3. DOPING STRUCTURE OF THE SEMICONDUCTORS An intrinsic semiconductor is a sufficiently pure semiconductor The most used semiconductors is silicium SILICIUM The silicium has like symbol Si In atoms of the semiconductors (germanium, silicon) the valence electrons is not free to move through the volume of the material, but they form a covalent bond that alloy with of atoms of the semiconductor in a crystalline structure. For effect of the breach of the covalent bond in the semiconductor two types of charge carriers are originated. Free electron are negative electric charge while hole are positive electric charge CONDUCTIVITY OF THE SEMICONDUCTORS In semiconductors there are two types of current. The first type of current is the classic electric current drift current, the second one happens for the phenomenon of the spread electrical worker. DOPING There are two types of doping: •P-TYPE •N-TYPE It is possible to add very small amounts of certain impurities such as arsenic or phosphorus which have more electrons per atom than silicon. In this way extra free electrons are produced that can move and form an electric current. These semiconductors are known as N-TYPE semiconductors becuase of the negative charge of the electrons Another type of semiconductors is formed by adding small quantities of other impurities such as aluminium or gallium which have fewer electrons per atom than silicon These impurities take electrons away from a few atoms of the semiconductors, increasing the number of holes. These semiconductors are called P-TYPE Referring to the positive charge associated with the holes.