* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lect5-CombinationalLogic
Propositional calculus wikipedia , lookup
Jesús Mosterín wikipedia , lookup
Modal logic wikipedia , lookup
Fuzzy logic wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical logic wikipedia , lookup
Curry–Howard correspondence wikipedia , lookup
History of logic wikipedia , lookup
Law of thought wikipedia , lookup
Combinatory logic wikipedia , lookup
Laws of Form wikipedia , lookup
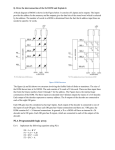
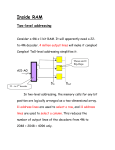
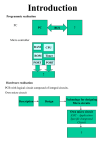
1 CPS3340 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 5: Combinational Logic Instructor: Ashraf Yaseen 09/10/2013 DEPARTMENT OF MATH & COMPUTER SCIENCE CENTRAL STATE UNIVERSITY, WILBERFORCE, OH Review Last Class Basic of Logic Design This Class Integrated Circuits Decoder Multiplexor PLA ROM Don’t Care Bus Next Class Design of ALU Integrated Circuit Integrated Circuit (IC) A small electronic device made out of a semiconductor material Classifications SSI (small-scale integration) MSI (medium-scale integration) 3,000~100,000 electronic components per chip VLSI (very large-scale integration) 100~3,000 electronic components per chip LSI (large-scale integration) up to 100 electronic components per chip 100,0000 to 1,000,0000 electronic components per chip ULSI (ultra large-scale integration) More than 1 million electronic components per chip Decoder Decoder logic block that has n-bit input and 2n outputs, where only one output is asserted for each input combination If the input is i (in binary), A then output i is 1 others are 0 Decoder Example 3-8 Decoder Multiplexor Multiplexor A selector The output is selected by an input control Implementation of a Multiplexor n-input Multiplexor A Multiplexor can have n-inputs Require selective inputs Implementation of an n-input Multiplexor Two-level Logic Try to Remember: Any Boolean Logic function can be implemented with only NOT, AND, OR functions We can also find that all logic functions can be written in a canonical form, in 2 levels Sum of Product Logical Product Sum (OR) of terms joined by Product (AND) of Sum Logical Product (AND) of terms joined by Sum (OR) Example Consider a logic function Equivalent to sum of products Equivalent to product of sums In Class Exercise Considering the following truth table for D, write the function of D using sum of products Answer Combinations that D is 1 Answer Programmable Logic Array Programmable Logic Array (PLA) Two An stages of logic array of AND gates (product terms) An array of OR gates PLA Example Considering the following table, implement the PLA for D, E, F PLA Example – cont. 15 A PLA can directly implement the truth table of a set of logic functions with multiple inputs and outputs. Each entry where the output is true requires a product term there will be a corresponding row in the PLA Each output corresponds to a potential row of OR gates in the second stage Another PLA Representation Dot in the AND plane Input, or its inverse, occurs in the product term Dot in the OR plane Corresponding product term appears in the corresponding output Read Only Memory Read Only Memory (ROM) Has a set of locations that can be read Contents of these locations are fixed Programmable ROM (PROM) Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM) Can be burnt using a device called a “ROM programmer” Data in the ROM can be deleted under ultra-violet rays EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Read Only Memory) Data in the ROM can be erased by a simple electric current ROM Height m inputs 2m addressable entries (input lines) Width n outputs (functions) 2n output bits mxn is the shape of the ROM ROMs and PLAs PLA is partially decoded ROM is fully decoded Contains a full output word for every possible input combination Always contain more entries than PLA PLA (7 entries) ROM (8 entries – 1 unused) Don’t Care Don’t Care We don’t care about the actual values Output Don’t Care We don’t care about the value of an output for some input combination Input Don’t Care An output only depends on some of the inputs Advantages of Don’t Care Easier to optimize the implementation of a logic function Example of Don’t Cares Original Truth Table Example of Don’t Cares Output Don’t Cares Input Don’t Cares Array of Logic Elements Bus In logic design, a collection of data lines that is treated together as a single logical signal Shared collection of lines with multiple sources 32-bit wide 2-to-1 multiplexor Summary Integrated Circuits Decoder Multiplexor PLA ROM Don’t Care Bus What I want you to do Review Chapter 1