* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic monuments in Kosovo wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
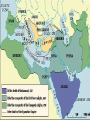
Chapter 10 The Islamic World Rome’s Three Heirs Byzantium Islam Latin Christendom Islam Arabs before Muhammad Polytheism Kaaba, a pilgrimage shrine located in Mecca, in which the sacred Black Stone (probably a meteorite) is housed. Politically disunited The Prophet Muhammad c. 570: Birth of Muhammad c. 610: Mohammed’s conversion; revelations from Gabriel 622: The hijra (“migration”) Muhammad fled to Medina First year in Muslim calendar 630: Muhammad captured Mecca 632: Muhammad died. Orthodox Caliphate 632-661 (the first four caliphs) 634-644: Omar 634: Conquest of Damascus 636: Conquest of Jerusalem and Persia 640: Conquest of Egypt The Expansion of Islam, 622 - ca. 750 http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/44cdc9b11080f6cc70ca.jpg Omayyad Caliphate (Damascus) 661-750 Conquest of North Africa and Spain. Abbasid Caliphate (Baghdad) 750-1258 1258: Mongols sacked Baghdad. Abbasid Caliphate ended. Two Governing Orientations Umayyads Westward Damascus 661-750 vs. Abbasids Eastward Baghdad 8th-10th centuries Omayyad Emirate in Spain 756-1031 1056: Ferdinand I of Castile proclaimed himself “Emperor of Spain,” beginning the “Reconquista.” 1492: End of the Reconquista in Spain. The Ottoman Empire 1350-1918 1453: Constantinople was conquered. 1914: The Ottoman Empire entered World War I 1919-1924: End of the Ottoman Empire References http://campus.northpark.edu/history/W ebChron/Islam/Islam.html http://campus.northpark.edu/history/W ebChron/Islam/Beliefs.html Islamic Culture Allah = God Islam = submission to God’s will Muslims = those who submit Jihad = the struggle to lead a virtuous life and to further the universal mission of Islam through teaching, preaching, and when necessary, warfare. Religion Strict monotheism. Emphasis on personal morality set by the Quran (or Koran; literally, “recitation”). Absence of clergy. Five Pillars of Faith (1) Declaring the central belief: “There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is the Messenger of God.” (2) Saying prayers five times a day (3) Almsgiving (4) Fasting from dawn until sunset during the sacred month of Ramadan (5) Making the pilgrimage to Mecca Government Theocracy: government and religion are inseparable. Caliph: the supreme religious and political leader of all Muslims. Scholarship Arab scholars preserved hundreds of ancient Greek manuscripts, copying and editing them in Arabic translations (Fiero 227). Scholarship The fund of scientific and technological knowledge, along with Arabic scholarship on Aristotle, stimulated a rebirth of learning in the 12th century and contributed to the rise of Western universities (Fiero 227). Literature Poetry: Romantic love was a favorite subject, which had profound influence on the medieval romance (troubadour poetry) and the Renaissance poet Petrarch (Fiero 228). Literature Sufi Poetry: A sufi is an ascetic Islam mystic who seeks to hold communion with the deity through contemplation and ecstasy. “Whatsoever I say in exposition and explanation of Love, when I come to Love itself I am ashamed of that explanation.” (Rumi) Literature Prose: The Thousand and One Night Islamic Art Taken from http://www.victorynewsmagazine.com/Arabesque.htm Idolatry Is Forbidden. Calligraphy Arabesque Thus, depiction of foliage in its varied forms became a very prominent feature of Arabesque art. One can visualize a strong link between art and nature in Islamic monuments where scrolling vines, surreal flowers and gracefully flowing leaves can be seen everywhere . . . . Inspiration The single most important factor that influenced the creation and evolution of Islamic Art is the Quran itself. One can find many verses in the Quran mentioning the beauty and abundance of Paradise with its exquisite gardens beneath which rivers flow. Geometric Forms Islam and science were never seen as two separate subjects. From the Islamic viewpoint, geometry is one of the streams that flows from the Fountainhead of Islam. This belief that science is an integral part of Islam led to many discoveries and advancements in the field of mathematics by Muslims. Islamic Art is therefore characterized by a beautiful combination of artistic foliage designs with geometric principles. The combination creates exquisite works of art unique only to the Islamic Cultural heritage. Regulating Principles Repetition Infinite extension The looping together of motifs to form a meandering, overall pattern (Fiero 231). Arches of the Great Mosque, Córdoba, Spain, begun 784-787. White marble and red sandstone, http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/08fcc1f55767cf1eb258.jpg Court of the Lions, Alhambra palace, Granada. Mid-14th century. http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/727024f6dfff6a69cf5f.jpg Sinan the Great, Mosque of Suleyman I, Istanbul, Turkey, begun 1550. http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/f7e3dee5e1758fc86ce5.jpg http://www.greatbuilding s.com/cgibin/gbi.cgi/Suyleman_M osque.html/cid_172334 3.html Sinan the Great. Interior of the mosque of Suleyman l, Istanbul, Turkey. http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/274a26e864a3c729b69a.jpg Entry portal, Shah Mosque, Isfahan, Persia (Iran), 16111666. http://mh1.xplana.c om/imagevault/uplo ad/b33a2d8234165 78dce23.jpg The End