* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The World of Islam
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Protestantism and Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
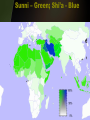
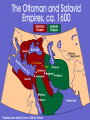
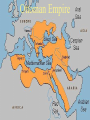
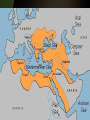
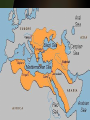
Quick Check • What happened to Muhammad’s parents? • Is Islam Mono or Poly theistic? • What job did Muhammad have? • What were the two major cities on the Arabian Peninsula? The World of Islam Chapter 26 Arabian Peninsula Before Islam • • • • • Polytheistic – animism Bedouins – nomadic people Oral history Judaism & Christianity Mecca – leading town – Diffusion – goods, people, • Kaaba – place of worship in Mecca – Filled with Idols – Sacred Stone – black stone Islam • Monotheistic – like Judaism & Christianity • Began in 7th century • Written History – Arabic Language • Prophet – Muhammad, wife Khadija • Book – Koran, Qur'an • 5 pillars The Rise of Islam • The Arabian Peninsula was a major trade route with many travelers • Mecca and Yathrib were leading trading towns • Mecca was the home of the Kaaba • Kaaba: sacred shrine of Arabs Kaaba • Built by Abraham - Jewish • Pilgrims flocked to the Kaaba • It contained images of Arab gods • And the Sacred Black Stone • Black Stone – Arabs believe it is a meteorite from heaven • http://www.metacafe.com/watch/70 1230/circling_the_kaaba/ The prophet Muhammad • Born in Mecca about 570 • Orphaned and raised by an uncle • Worked as a caravan leader for a rich woman named Khadija • She encouraged him to fast and pray in the desert Muhammad • During one retreat he heard a message from the angel Gabriel • He was told to preach to the people • Khadija encouraged him to do as he was instructed Islam Questions • List and describe the 5 Pillars of Islam • What is the Koran? • Who are the People of the Book? • List ethical standards Muslims must follow • Why did Islam expand? 3 reasons • What are the two branches of Islam? • When did the division in Islam occur? Islam – Empire of Faith 1. 2. 3. 4. What is the hejira? Identify Yathrib & Medina Who are the People of the Book? Why did the people of Mecca fight Muhammad and the people of Yathrib/Medina? 5. How did Muhammad gain control of Mecca? 6. What happened to the Kaaba after Muhammad gained control of Mecca? Islam – Empire of Faith • Why does Islam spread rapidly? • Why does Islam divide after Muhammad’s death? • Does Muhammad’s death help Islam spread? • List 10 Great Achievements of Early Muslim Empires • How did the Crusades unify Muslims? • List strengths of the Ottoman Empire • List Great Ottoman Leaders Quick Review • What does Islam - اإلسالم- mean in Arabic? • Why did Islam split after Muhammad’s death? • What are the two branches of Islam? • What event brought anti-Muslim feelings in Europe? Islam Class Work • Vocab • Religion Comparison Chart • Religion – Belief in God, 5 Pillars, Koran & Tradition, People of the Book • Art, Architecture, Literature • Algebra & Trigonometry, Engineering, Astronomy, Medicine • People – Muhammad, Saladin, Mamun, Rumi, Mehmed, Suleyman Islam Questions • List achievements of the Arab Empires (Umayyad & Abbasid) • Where was the center/capital of the Umayyad Dynasty? • Where was the center/capital of the Abbasid Dynasty? • Who is Muhammad al-Razi? • What trade routes helped usher in the Golden Age of Islam? • What advances in learning came from the Golden age of Islam? Muhammad • He won few converts, Arabs were polytheistic • Town leaders did not people to stop making the pilgrimage to the Kaaba • He was kicked out of Mecca when Khadija died • Muhammad was welcomed as a leader in the city of Medina Islam: the people • • • • Qur'an, Koran – Muslim Holy book Islam – means submission ~1.2 billion Muslims in the world; 22% Caliph – successor to Muhammad – Sunni – election from religious leaders 90% of Muslims worldwide – Shi’a – descendent of Muhammad • Imam – prayer leader • Ayatollah – important Shi’a clergyman • People of the Book – Christians and Jews The 5 Pillars • • • • One God Prayer – 5 times a day Charity Pilgrimage – to Mecca once in your life • Fasting – During Month of Ramadan Sunni – Green; Shi’a - Blue Foreign Invaders to the Middle East • Seljuk's – Muslims from Turkey – Seized Baghdad – Weakened Byzantine Empire • Mongols – From Central Asia – Defeated Seljuk's for Baghdad – Led by Genghis Khan – Converted to Islam Foreign Invaders to the Middle East • Crusaders – From Europe – Fought for control of holy land, Jerusalem – Muslims retained control • The beginnings – 5 pts Islam Review – Mecca, Kaaba (sacred shrine for polytheistic Arabs), Centers of Trade, People of the Book • Muhammad/Leaders – 5 pts – Orphaned & raised by uncle, trader, Khadija (wife), not liked in Mecca because of monotheistic beliefs, flees Mecca and goes to Medina, Hejira – Saladin – Soldier – Mamun – Scholar – Sulyeman – Sultan • Beliefs/Pillars – 5 pts – 5 Prayers, Pilgrimage, 1 God, Fasting, Charity • Achievements – 5 pts – Hospitals, algebra, germs cause disease, medicine, scientific method, eyes and , cataracts, lenses & surgery, engineering, House of Wisdom, writing, numbers • Sects/Invaders – 5 pts – – – – – Sunni – caliph can be any elected leader – 90% Shi’a – caliph needs to be descendent of Muhammad – 10% Seljuks – Turkey – capture Baghdad (Fertile Crescent) Mongols – Central Asia – capture Baghdad (Fertile Crescent) Crusaders – Europe – capture Jerusalem (Fertile Crescent) The Two Empires • The Ottomans – Turks – Sunni • The Safavid – Persians - Shiite Safavid Empire • Rivals of the Ottomans • Shah – Leader of Safavid Empire • Abbas the Great – most famous leader • Strengths – same as Ottomans • Modern Day Iran Person Saladin* Mamun* Rumi Mehmed Suleyman* Achievement (profession & successes) Person Saladin* Mamun* Rumi Mehmed Suleyman* Achievement (profession & successes) Profession – King & Soldier • Hero of the Crusades for Muslims • Captured Damascus (syria), Aleppo , Mosul (Iraq) Profession - Caliph & Governor, SCHOLAR • Translated books in to Arabic Profession – • Wrote largest collection of Poetry in ME Profession – • • • Conqueror Extended Ottoman Empire & reorganized territories Established Code of Laws Profession • Poet Sultan – Leader/King Architecture – Fix Dome of the Rock Reorganized set of laws The Ottoman Empire Great Ottoman Sultans • Sultan – Arabic word for Strength or Power • Osman I – 1299-1324 – Ottoman Empire named after him • Mehmed II – 1451-1481 – Ruled twice & Conquered Constantinople • Suleyman I – 1520-1566 – Longest ruling Sultan • Mehmed II FATİH (The Conqueror) – Conquered Constantinople in 1453 – Converted Hagia Sofia, Christian Church into Muslim Mosque • Suleyman I MUHTEŞEM (The Magnificent) or KANÛNÎ (The Lawgiver) The Ottomans were: •Turkish (capital Istanbul) •Muslim •The largest empire in the world Five Ottoman Strengths: 1. Respected people they conquered (millett) 2. Fearless army 3. Always improved technology 4. Control Trade 5. Strong Leaders The Ottoman Government • Empire reigned 600 years, until end WWI • Sultan – led with absolute power • Men of the Pen • Men of the Sword Ottoman Empire What was the source of Ottoman power? 1. Control of Trade •Location on the east/west trade route •Control of the Waterways 2. Wealth from trade 3. Superior technology (the benefit of diffusion) How did the empire end? The Europeans destroyed their strengths. Ottoman Strengths #1: Control of trade •Europeans broke this strength by going around Africa and gaining control of trade. Ottoman Strength #2: Wealth •Discovery of the New World leads to fantastic wealth for Europe from Aztec and Inca gold and silver. Ottoman Strength #3: Technology •The industrial revolution surpassed the Ottoman superiority in technology especially in production of guns and munitions and other products necessary for war. The Empire Ends Three reasons: 1. Nationalism: People ruled by the Ottomans wanted independence. •Europeans: Serbs, Croats, Bulgarians, Greeks. •Arabs 2. European Imperialism: •Industrial revolution caused a need for raw materials •European industries wanted new markets •Large navies developed by Europe to control trade 3. Competition between European nations led to WWI in 1914 The Ottomans sided with Germany and lost. The Arab territories were divided up between Great Britain and France. Turkey became a republic The Balfour Declaration •Great Britain promised the same land to the Jews and the Palestinian Arabs. Patterns of Life – page 580 Village 1. sheep and goats 2. Setup near water (river, oasis, coast, lake) 3. Farming – wheat olives 4. Men and women, specialize jobs Nomadic 1. Moved from oasis to oasis 2. Lived with few resources 3. Fights all the time 4. known and Bedouins* City 1. Protected by high walls 2. many cities developed 3. suq (markets) 4. mosque Family (more important than individual) 1. Patriarchal – controlled or ruled by men/ Matriarchal- women 2. Arranged marriage 3. Divorce easier for men (3 times) 4. Men can have 4 wivesprovide equally 5. Children must obey their parents Women • Had to obey fathers -> husband -> oldest son (Subordinate) • Modest and secluded within home • Wore certain clothingveiled face (custom from India) • Education • Right to own property Conclusion Page 583 1, 3, 4, 5 Patterns of Life – page 580 Village 1. 2. 3. Family-Center of the village culture. Patriarchal-Ruled by father Jobs-Specialized jobs Houses-Small, made of mud bricks. 4. Family 1. 2. 3. Arranged marriages a man can have up to 4 wives divorce is easier for men then women Nomadic 1. Lived in small tribal groups 2. Constantly on the move 3. Lived with scarce sources of water 4. Bedouins 5. Nomads often came into contact with government and villagers 6. 7. 8. City 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. High city walls and narrow streets Suq was the market place Mosques were the center of life Domascus old trading city Women Conclusion 1. Had to obey men Page 583 < awesome. 1, 3, 4, 5 2. concealed bodies from other men 3. had a right to •Page 2 – Nomadic Life: Bedouin, Highland Nomads, conflicts •Page 3 – City Life: reasons for development, major cities, mosques, suq •Page 4 – Family Life: Koran, marriage, divorce •Page 5 – Women’s Lives: Koran, mothers, women’s rights Review ?s •Page 583 •3 •4 •5 On the Test • Islam • Centuries of Turmoil – Conquerors of ME – Ottomans/Safavids – Golden Age • Patterns of life • Imperialism & Nationalism – – – – Egypt Iran Turkey Palestine Test Questions Writing Section 1&2 Three Nations Modernize Egypt Turkey When did they become independent? Who was famous leader? Review Questions on Palestine Page 588 1, 3, 6 Vocabulary Review Page 589 Vocab 1-5 Iran Turkey Becomes a Country • The Turks created their country after WWI • Kemal Ataturk abolished the Ottoman Empire and made Turkey a Republic • Ataturk means ‘Father of the Turks’ Ataturk’s Reforms • The government built industry • Separate church and state (secular) – Western law replaced Islamic law – Women could vote and hold public office – Public schools separate from religious schools • Turkey began using the western calendar, alphabet, clothing (no veils in public) Egypt • Egypt became a battle ground between the British and French • Both countries wanted to build a canal across the Isthmus of Suez • Muhammad Ali: Fought against the French; became governor of Egypt Ali’s Reforms • Brought in Europeans to teach military tactics and scientific training • Improved farming techniques; introduced cash crops (tobacco, cotton, sugar) • Crushed Egyptian economy because he borrowed too much money from European countries France & Britain control Egyptian Economy • France won the right to build the Suez Canal in 1859; Canal opened 1869 • Britain bought control of the Suez Canal to help the Egyptian government • Egypt wins independence in 1922 • Egypt gains control of the Suez Canal from Britain in 1956 Iran • Britain and Russia competed over Iran to gain access to the Persian Gulf • Reza Khan led the Iranians to remove foreign control of his country • Under his direction Iran adopted western culture – Clothing, women’s rights, education, government Palestine/Israel • Great Britain controlled Palestine 20’s & 30’s • Jews wanted to return to Jerusalem since the Diaspora of 70 A.D. • Jews faced anti-Semitism as they tried to create their own state • Theodor Herzl led the Zionist movement, movement to create a Jewish state Balfour Declaration • A British document which declared Palestine as the national home for the Jewish People • The document also said “…nothing should be done which may prejudice the civil and religious rights of existing non-Jewish communities in Palestine…” • That meant Palestine belonged to Arabs because they lived there Arabs in Palestine • Wealthy Arab business men sold their farms to Jewish immigrants • Arab farmers fought against losing their land • Arabs attacked new Jewish settlements, Jewish people fought back • War comes to Palestine