* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CEE 437 Lecture 1
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geoprofessions wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
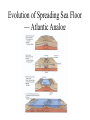
CEE 437 Lecture 1 October 1, 2002 Thomas Doe Outline • • • • • • Course Introduction Geology and Engineers Brief History of Geology Global Structure Plate Tectonics The Rock Cycle Topic Course Introduction, Earth Structure and Composition Minerals, Rock Cycle, Lab Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, Geologic Time Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks, Lab Geologic Maps and Stereonets Structural Geology Field Trip #1, Seattle Geology Physical Properties of Rocks and Soils Rock Mass Classification Indices Fracture Characterisation and Fractured Rock Analysis Rocks Slope and Tunnels Mid Term Field Trip #2, Cascadia Site Characterization, Borehole Characterization and Geophysics Landslides and Subsidence Earthquakes and Seismology Engineering Geology in Washington State Glacial Geology Thanksgiving Field Trip #3: Glacial Geology Hydrogeology I — Principles Hydrogeology II — Site Characterization Final Exam Geology — Brief History • Origins in late 18th and early 19th Centuries • Catastrophism and Uniformitarianism – Age of Earth – Uniformity of Processes • Plate Tectonics Revolution (1950’s to 1980’s) • Neo-Catastrophism Siccar Point Unconformity Smith’s Map of England Engineering and Geology • William Smith and the English geological map • Karl Terzaghi and insights to the distribution of earth materials • Earth heterogeneity!!!! Global Structure • Based mainly on seismic information and meteorite compositions • Crust ~25-75 km depending varyin under continents and oceans Global Structure Velocity Variation with Depth Development of Plate Tectonics • Evidence from ocean floor magnetism and ages • Evidence from seismicity • Evidence from cross-continent correlations of rocks Global Seismicity Benioff Zone Sea-floor Spreading • Mantle convection driven Seafloor Spreading — Sediment Ages Evolution of Spreading Sea Floor — Atlantic Analog Convergent Margins • Ocean to Continent • Continent to Continent Convergent Margin Rock Cycle Convergent Margin — Subduction Zone Major Crustal Plates Evolution of Continents — North American Craton North American Accretion