* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Continental_Drift_and_Plate_Boundaries_
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
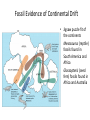
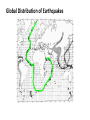
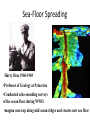
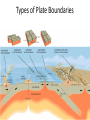
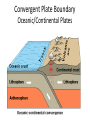
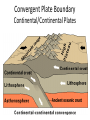
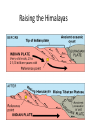
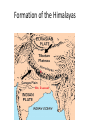
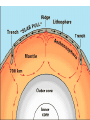
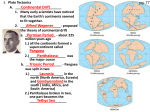
Alfred Wegener • 1880 - 1930 • Doctorate in planetary astronomy and an interest in meteorology • Proposed the Theory of Continental Drift in 1915 Theory of Continental Drift • Proposed by Alfred Wegener - 1915 • Continents started as a single landmass and split apart 200 million years ago • Not accepted by scientists as a valid theory Fossil Evidence of Continental Drift • Jigsaw puzzle fit of the continents • Mesosaurus (reptile) fossils found in South America and Africa • Glossopteris (seed fern) fossils found in Africa and Australia Rock Evidence of Continental Drift • Glacier evidence in warm weather places • Mountains in South America and Africa line up when the continents are together • Layers of rock in Antarctica, Australia, South America, Africa and India are similar. • Glacial till found in places • currently too close to the equator for glaciers to Connecting Glacial Evidence Problems With Wegener’s Theory •Could not explain the forces that moved the continents •Not possible for the continents to move through the ocean floor Technology & the 1950’s • Development of sonar during WWII – Mapping of the ocean floor – Discovered ruggedness of ocean floor • Development of submarines and submersibles – youth of ocean floor – Confirmation of reversals in the Earth’s magnetic field – sea-floor spreading hypothesis • Documentation of the locations of earthquake & volcanic activity Development of the Plate Tectonics Theory • Surface of the Earth is split into a series of plates which float on semi-molten rock • Convection currents in the mantle push the plates around on the surface of the Earth • Because of plate movements the surface of the Earth is constantly changing •Plate boundaries are where Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain ranges occur • Crust is made at mid-ocean ridges • Crust is destroyed at subduction zones Earthquake Zones Global Distribution of Earthquakes Sea-Floor Spreading Harry Hess 1906-1969 •Professor of Geology at Princeton •Conducted echo-sounding surveys of the ocean floor during WWII •magma oozes up along mid ocean ridges and creates new sea floor Divergent Boundary • Mid-Atlantic Ridge • Caused by sea-floor spreading • Rate of spreading averages 2.5 cm/yr • Has taken 100-200 million years to create the Atlantic Ocean Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent Plate Boundary Oceanic/Continental Plates Convergent Plate Boundary Oceanic/Oceanic Plates Convergent Plate Boundary Continental/Continental Plates Raising the Himalayas Formation of the Himalayas Hot Spots Around the World