* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
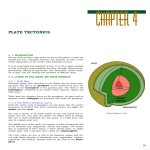
Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 Sections 1-3 Pgs. 96-110 Composition of Earth (p.96-97) Earth is composed of 3 layers: Crust (outermost layer) Mantle (middle layer) Even though it’s the thinnest layer, it’s too thick to drill completely through. 2 types- continental and oceanic Hot, convecting = Magma Can be studied when it pushes to the surface = volcanic eruptions Core (inner layer) made mostly of iron = very dense, metallic Physical Structure of Earth (p.98-99) Earth is divided into 5 physical layers Order from outermost to innermost Lithosphere- made of crust and upper mantle Asthenosphere- made of “plastic” part of mantle Mesosphere- made of strong part of mantle Outer Core- liquid layer of core Inner Core- solid layer of core 5 PHYSICAL LAYERS OF THE EARTH (p. 98-99) Tectonic Plates (p. 100-102) Pieces of Lithosphere that move around on top of the Asthenosphere (float like ice in a drink) Fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Not all plates are the same size Can be all oceanic (under water), but many are both oceanic and continental (some below water and some as a landmass) Mapping Earth’s Interior: Earthquake’s cause seismic waves that can be measured using a seismograph. Use these measurements to get descriptions of the parts of the Earth we can’t explore Continental Drift (p.104-106) Wegener thought all continents were once one, super continent = Pangaea Hypothesis states the single landmass broke apart and drifted to present locations Force that moves the continents is seafloor spreading- new lithosphere forms as magma rises to surface and solidifies Takes place at mid-ocean ridges Evidence for Continental Drift & Seafloor Spreading (p.104, 106) 1. Continental drift is supported through the finding of fossils and examining rock layers Plants and animals couldn’t cross the ocean continental edges must have met at one time Rock layers and evidence of ancient climates are similar on many continents 2. Magnetic reversals are recorded with magnetic minerals (iron) on ocean floor N & S poles change place Iron comes up in magma through mid-ocean ridges Plate Tectonics (p.108-109) Theory that Earth’s Lithosphere is divided into plates that move around on top of the Asthenosphere Caused by cycle of heating rock within the Earth: hotter rock rises then cools becoming more dense cooled rock sinks toward center again as it approaches the core, it heats again CALLED CONVECTION! Tectonic Plate Boundaries (p.109) 3 types of boundaries (boundaries are where tectonic plates touch) Type Definition Possible Outcome Convergent When 2 plates collide Divergent Transform Folds Faults Mountains When 2 plates separate Seafloor spreading Mid-ocean ridges When 2 plates slide past each other Earthquake