* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ocean Topography presentation
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
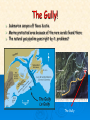
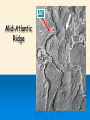
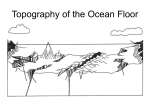
Physical Oceanography Ocean Topography What is Topography? The The physical features of an area shapes, patterns and physical configuration of the surface of the ocean basins Side-scan sonar is used to create an image of large areas of the sea floor. This tool is used for mapping the seabed in conjunction with seafloor samples it is able to show differences in material and texture type of the seabed. The ocean basin: Structures 1. Continental Margin: (near continent) 2. Deep Ocean Basin: Continental Shelf Continental Slope Continental Rise Submarine Canyons Abyssal Plains Oceanic ridges 3. Others: a Trenches b Seamounts and Guyots c Atolls Instructions: On the sheet provided, label the diagram and then copy the definitions You can yell at me tomorrow, but there will be LOTS of notes….then we’ll take a break from notes for a few days! Major Sea Floor Structures: A. Continental Slope B.Sea Mount D. Mid Ocean Ridge E. Island F. Continental Shelf C. Abyssal Plain G. Oceanic Trench H. Guyot Definitions (YES, COPY) Shelf – An extention of the continent under water. There is a fairly abrupt drop off at the edge. Has hills, valleys, canyons and other features. This is very wide off of Canada’s maritime provinces. (Grand Banks and Scotian Shelf) Continental Slope – The portion of the ocean bed between the edge of the continental shelf and the deep-sea floor. The average angle displayed by the slope is about 5 degrees. Continental Plain – The largest portion of the earth’s sea bed. It is covered with a thick layer of sediment, beneath which is relatively dense basalt rock. Vast, empty and usually boring. Abyssal Seamounts and Guyots Both are undersea volcanoes that originated at a hotspot or along a ridge Guyots once reached the surface of the ocean and have flat, eroded tops Seamounts never reached the surface, so they have pointy tops Example:Hawaii! Submarine Canyons V-shaped indentations in the continental shelf, usually ending in a fan shaped wedge of sediments. How do submarine canyons form? Thought to be fast moving currents and underwater landslides. The Gully! Submarine canyon off Nova Scotia Marine protected area because of the rare corals found there The natural gas pipeline goes right by it…problems? The Gully Mid-Ocean Ridge A large underwater mountain chain, part of a cast system extending some 40,000 miles through four of the world’s oceans Caused by divergent plate boundaries Us! Mid-Atlantic Ridge Trench – deep gap in ocean floor, formed by movement of plates. Ex: Mariana Trench is 10,668 meters deep They are among the most active areas on Earth.They are the deepest areas of the Earth’s crust. 90% of trenches are found around the Pacific rim. Arc – A series of islands of volcanic origin, usually found at or near the edge of an ocean basin. Island Atolls A ring shaped island of coral reefs and coral debris. These often form over sinking inactive volcanoes. Where are atolls? Most of the world's atolls are in the Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean The Atlantic Ocean has no large groups of atolls other than eight atolls east of Nicaragua