* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geology unit test project
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
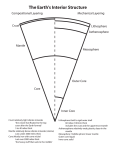
By Jordan Grant, Jeremy Marasco & Lauren Weir There are 3 types of mountains Folded-The folded mountains is when a convergent boundary collides. Fault-block- fault block landforms are formed when large areas of bedrock are widely broken up. And a dome mountain- a dome mountain is also when a convergent boundary collides. Convergent- the convergent boundaries is when the plats crash in to each other. The results are earthquakes, mountain formation, and volcanoes. The divergent boundary spreads apart. The results are volcanoes and sea floor spreading. The transform-fault is the fault that slide agents each other. The results are earthquakes. There are 3 types of rocks. Igneous Sedimentary. And metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed when magma below the surface cools an hardens into igneous rocks. Sedimentary rocks are sediments that are cemented together and are formed from tiny rocks, dirt, and cement. Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core We live on the crust. The crust is also called the lithosphere. Did you know, not one human has every dug through the crust? The crust ranges from 5-40 miles thick. The mantle is the thickest layer. The mantle includes the asthenosphere, where the convection currents take place. Now to the outer core. The outer core obviously, is the outer –core. It surrounds the inner core and is really hot. The outer core is made of metal and is really hot. The inner core is the hottest, and smallest layer of the earth. Even though it is the hottest, it is sold! From all of the layers above, it makes the inner core solid from all of the pressure. Exosphere Thermosphere Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere The first layer of the atmosphere , closest to earth, is the troposphere. The troposphere contains all weather and life. The second layer is the stratosphere. The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, that protects us from the suns UV rays. Some jets fly here to avoid bad weather. The Next layer is the mesosphere. The mesosphere is where the meteors burn/ freeze up. Here, the air is very thin The thermosphere is the 4th layer. The air is very thin . In the thermosphere, satellites orbit the earth in this layer. The thermosphere is the thickest layer. The exosphere is not really a layer, ( some people call it a layer) but it is considered outer space. Lithosphere Hydrosphere Aesthenosphere The lithosphere is basically all of the land on earth. It includes all islands, plains, mountains, and more. The hydrosphere is all of the water on earth. From rivers, to oceans, even in your shower! The aesthenosphere is in the mantle. The aesthenosphere are the convection currents , the swirling pools of magma in the mantle. The magma circles from the core, up to the crust as it heats and cools. Lauren Weir- Earth’s spheres, layers, and atmosphere Jeremy M.-Rocks, Jordan G.- Mountains, Plate tectonics/ boundaries.