* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 27 Study Notes
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
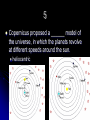
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
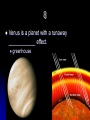
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Study Notes: Chapter 27 Planets of the Solar System 1 The early oceans became ______ when dissolved solids were carried from land into the oceans. salty 2 About ____ of all matter contained in the solar nebula now exists in the sun. 99% 3 Small bodies that orbit planets are called ________. moons. 4 When early Earth’s atmosphere formed, and hydrogen gases were lost because Earth’s _____ was too weak. helium gravity 5 Copernicus proposed a ______ model of the universe, in which the planets revolve at different speeds around the sun. heliocentric 6 Mars’s volcanoes are _______ than those of Earth because Mars has no moving tectonic plates. larger 7 Impact ______ are caused by collisions with _______ in space. craters objects 8 Venus is a planet with a runaway ____________ effect. greenhouse 9 The factors that contribute to Mercury’s daily temperature fluctuation of about 600°C are the planet’s slow ______ and it is the closest planet to the ____. rotation sun. 10 A region of the solar system just ________ Neptune’s orbit, which contains small bodies made mostly of ice, is called the ______ belt. beyond Kuiper 11 Neptune’s Great ______ ______ is a giant _________. Dark Spot storm. 12 The least _______ planet in the solar system is ______. dense Saturn 13 The right combination of ______, ______, and _______ supports life on Earth. temperature water oxygen 14 Kepler’s first law states that planets orbit the sun in paths called ________. ellipses. 15 Young Earth formed a core, mantle, and crust in a process called _________. differentiation 16 _____ is a planet which has _____ regions that may still be active. Mars volcanic 17 The early ______ developed when many volcanic eruptions released large amounts of gases in a process called __________. atmosphere outgassing. 18 _____ is the planet that has _____ like Earth’s because its axis tilts at an almost identical angle. Mars seasons 19 A rotating cloud of gas and dust from which Earth’s solar system formed is called a solar _____. nebula 20 When the solar system formed, smaller bodies joined together through collision and the force of ______ to form larger bodies called _________. gravity protoplanets. 21 Jupiter’s Great ____ Spot and _______ Great Dark Spot are both raging _______. Red Neptune’s storms. 22 Around the ______ of Earth is an iron- and magnesium-rich rock layer called the _______. core mantle. 23 ________ that circle stars other than Earth’s sun are called __________. Planets exoplanets 24 The ______ belt can be found between the planets _____ and Jupiter asteroid Mars 25 Small bodies from which planets originated during the early ______ of the solar system are called ___________. formation planetesimals. THE END