* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
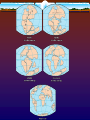
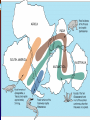
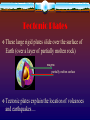
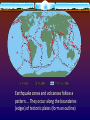
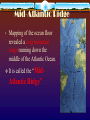
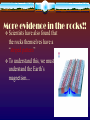
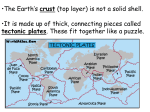
12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift Wegener came up with the continental drift theory • the idea that the continents used to be connected as one big supercontinent but slowly moved apart over time He named the original supercontinent Pangaea. Pan - gaea “all” “Earth” Putting the Pieces Together... continents do not fit “perfectly” like a jigsaw puzzle. A better fit is found by matching the continental shelves (original shorelines that are now underwater) The Geological/ Rock Evidence Mountain ranges of one continent, end at coastline begin again at another continent (similar folds, ages) Geological/ Rock Evidence Similarities between rocks of adjacent continents are evidence for continental drift. The rocks found in Newfoundland are the same type and age as rocks found in Greenland, Ireland, Scotland, Norway. Fossil Evidence The fossils of some ancient species suggests evidence for ‘pangaea’. Wegener found fossils of a fresh-water reptile ‘Mesosaurus’ in two places: - SE South America and SW Africa This small freshwater reptile could not have swam this distance. Fossil Evidence Glossopteris (a fern) Found In: South America Africa Australia India Antarctica Fossil Evidence Problem: Ferns do not grow in cold climates (Antarctica) Glacial Evidence Evidence of glaciers formed in ice ages provides support to CD theory During ice ages, glaciers covered large areas of land When the glaciers retreat/ advance, they leave behind proof Deeply scratched rocks (striations), U-shaped valleys, patterns of rock formations “Paleoglaciation” More Evidence Coal Deposits in Antarctica - - Coal forms from dead matter (usually tropical swamp material) Since the South Pole has never had a tropical climate....it must have been in a warmer location than it is now Provincial Exam Question Provincial Exam Question How the Continents Moved The current theory is that the continents moved due to the movement of tectonic plates. Tectonic plates = movable slabs of rock that make up the Earth Tectonic Plates These large rigid plates slide over the surface of Earth (over a layer of partially molten rock) magma partially molten surface Tectonic plates explain the location of volcanoes and earthquakes.... Volcanoes/ Earthquakes Volcanoes are openings in the Earth’s surface that spew gases, chunks of molten rock Earthquakes are sudden, ground-shaking releases of built up energy under Earth’s surface Earthquake zones and volcanoes follow a pattern.... They occur along the boundaries (edges) of tectonic plates (form an outline) Mid-Atlantic Ridge • Mapping of the ocean floor revealed a long mountain range running down the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. It is called the “Mid- Atlantic Ridge” How it was formed... The tectonic plates of the Earth slide apart (sliding is called “conduction”) Another way to think of this is “seafloor spreading” Something must replenish this lost crust! Occurs at rate of ~ 1 inch /yr Magma to the Rescue!!!! Areas of oceanic crust are replenished by volcanic activity.... Magma (molten rock) rises up Cools and hardens when it reaches surface Forms the new sea floor Magma and More Magma This process keeps going..... Convection currents cause more magma to rise Magma forces apart hardened material Older rock is pushed aside as new rock forms! “Sea Floor Spreading” Spreading Ridge An animation.... Proof of Sea Floor Spreading! In the 1940’s...oceanographers took samples of rock from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge - Younger rocks were found closer to ridge - Older rocks were found farther from ridge (and in thicker layers...built up!) Provincial Exam Question More evidence in the rocks!! Scientists have also found that the rocks themselves have a “striped pattern” To understand this, we must understand the Earth’s magnetism.... Earth’s Magnetic Field N geographic Pole S geographic Pole Every few thousand years....the direction of magnetic field REVERSES! “MAGNETIC REVERSAL” Consider a rock..... Rock contains metals like iron (Fe) Little pieces of iron “line up” with magnetic field and then they STAY that WAY! When MAGNETIC REVERSAL happens...they line up in opposite direction! Rocks “preserve” the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field that existed when the rock formed! Amazing! Studying the magnetic properties of ancient rocks.... “Paleomagnetism” Back to the Sea Floor.... So the sea floor is spreading and new rocks (from magma) are formed... Looking closely at the sea floor, scientists found a striped pattern! “magnetic striping” Provincial Exam Question A HOT SPOT.... A geological area where molten rock rises to Earth’s surface! Provincial Exam Question HOT SPOTS.... Hawaiian Islands were formed by a tectonic plate passing over a hot spot. The plate slides in the direction of the arrow.... Forms a CHAIN of islands! Take the Section 12.1 Quiz