* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
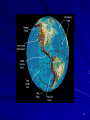
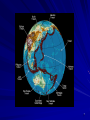
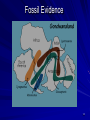
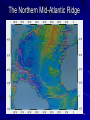
Lecture #04 Plate Tectonics Overview 1 By plate we really mean a “shell” on Earth’s surface that is about 100-200 km thick and includes all of the crust, and the uppermost part of the mantle. Tectonics is the term we use in geoscience to represent the formation of folds, fractures, faults, etc. in rocks. 2 Global Seismicity 3 Inter- and Intraplate Earthquakes Most earthquakes occur along plate margins because plate margins are relatively weak, but about 10% of earthquakes occur within the interior of plates. We classify earthquakes depending on where they are located Interplate - between plates Intraplate - within plates 4 5 6 7 The Shape of the Continents As soon as good maps became available, people noticed the similarity between the shape of continents, most notably, South America and Africa. 8 Map from 1650 9 Map from 1676 10 Map from 1893 11 Modern Day Map 12 Alfred Wegener Most people thought the complementary shapes were coincidence. Alfred Wegener was an exception who sought more evidence that the continents had been joined. He found it in the rocks & fossils and proposed the hypothesis of Continental Drift. 13 Fossil Evidence 14 Wegener’s Problem The problem with the Continental Drift Hypothesis was that Wegener had no mechanism for moving the continents through the ocean floor. Powerful physical arguments prevented continental drift from acceptance by the majority of scientists, particularly those in the northern hemisphere. 15 Paleomagnetism Wegener died in 1930 with his hypothesis largely ignored. But despite the problems and an overwhelming rejection of his ideas, not everyone forgot about his work. In the 1940’s and 1950’s geophysicists studying the record of Earth’s magnetic field began to revive some of the ideas to explain observed variations in their observations. 16 Discoveries in Marine Geology During WWII and with the initiation of the Cold War, much research was focused attention on the ocean floor. – Researchers were surprised to find long, large mountain chains and deep trenches. – They also found that the rocks which compose the ocean floor were young, ranging in age from recent to 200 Ma. 17 Sea-Floor Spreading Sea Floor Spreading is the hypothesis in which new ocean floor is created at the mid-ocean ridges and that plates move apart at the ridges and the continents move with them. 18 The Northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge 19 Sea-Floor Recycling Since new material is created at the mid-ocean ridges and Earth is not expanding, somewhere material must be removed from the surface. It turns out that old ocean floor is “subducted” into the mantle at subduction zones. 20 South America to Africa 21 Western Pacific Subduction Zones 22 Geology & The Plates Plates play an enormous role in geologic activity. Much of the action in geology occurs along the plate edges, or boundaries. The boundaries are the locus of – Earthquakes – Volcanoes – Heat loss – etc. 23 The Major Plates 24 Summary Plate tectonics is our best model for how the outer part of Earth contributes to the planet’s thermal processes. Plate tectonics is the surface manifestation of convection (think lava lamp) that the Earth undergoes to cool itself. 25 Summary (cont.) A central point to plate tectonics is that lateral movements are dominant over vertical movements. In other words, the “drifting” of continents is much faster and more significant than the uplift of mountains. 26 Summary (cont.) Evidence for plate tectonics is overwhelming: – Seismicity patterns – Magnetic lineation on the sea floor – GPS measurements – Fossil evidence – Many,many other lines of evidence 27