* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2: Earth as a System STUDY NOTES Chapter 2 Section 1
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
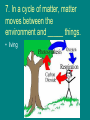
Chapter 2: Earth as a System STUDY NOTES Chapter 2 Section 1: Earth: A Unique Planet 1. Earth’s circumference is about 40,000 km, and its shape is an ________ ___________. • oblate spheroid 2. According to the law of gravitation, the force of attraction between two objects depends on the masses of the objects and the __________ between them. • distance 3. The lower boundary of Earth’s crust is called the ________. • Moho 4. The solid, plastic layer of the mantle is called the _________. • asthenosphere 5.The force of attraction that exists among all matter in the universe is called _________. • gravity 6. The mesosphere is the strong, lower part of the _______ between the asthenosphere and the outer core. • mantle 7. The _______ is the thin and solid outer most layer of the Earth above the mantle • crust 8.The lithosphere is the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the ________. • mantle 9. The ________ is the central part of Earth below the mantle. • core 10. The _______ is the layer of rock between Earth’s crust and core. • mantle Chapter 2 Section 2: Energy in the Earth System 1. Evaporation, condensation, and precipitation are part of the _____ _______. • water cycle 2. Plants capture and transfer solar energy in a process called ___________. • photosynthesis 3. Because Earth’s interior is warmer than its surface layers, hot materials move toward the surface in a process called ________. • Convection 4. The largest ecosystem on Earth is the ________. • biosphere 5. In general, ecosystems react to change by _____ _______. • restoring • balance 6. The transfer of energy throughout an ecosystem begins when plants capture solar _____ through photosynthesis. • energy 7. A community of organisms and their abiotic environment is called an ___________. • ecosystem 8. The _____ is the part of Earth where life exists. • biosphere 9. The ____ is a mixture of ____ that surrounds a planet or moon. • atmosphere • gases 10. The _____ is the portion of Earth that is water. • hydrosphere 11. The _____ is the mostly solid, rocky part of Earth. • geosphere 12. An open system is a system in which both matter and energy are _____ with the surroundings. • exchanged Chapter 2 Section 1 green book: The Cycles of Matter 1. All organic molecules contain __________. • carbon 2. Bacteria in soil change nitrogen gas into other forms in a process called ____ ______. • nitrogen fixation 3. Carbon is stored as a type of rock called ______ in the______. • carbonate • geosphere 4. Carbon moves between the environment and living things in the _______ _______. • carbon cycle 5. ______ is transferred between systems, but it cannot be created or destroyed, according to the _____ law of thermodynamics. • Energy • first 6. Groundwater is an important part of the _______ cycle. • water 7. In a cycle of matter, matter moves between the environment and _____ things. • living 9. Most animals get the carbon they need by ______ plants. • eating 10. Organisms need _______ to build proteins for DNA. • nitrogen 11. _________ is when plants use carbon dioxide to make sugars. • Photosynthesis 12. The sun, internal convection, and gravity are important sources of ________ in the Earth system. • energy 13. Transpiration is one part of the _______ cycle. • water The End!!!