* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of Continental Drift, part 1
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
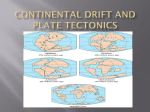
The History of Continental Drift 1. Plate Tectonics defined. 2. What did Plate Tectonics replace? 3. Alfred Wegener and Continental Drift. Evidence Theory Outcome Lithospheric Plate: Pieces of crust that move independently of neighboring plates Tectonics: dealing with structural features of the Earth (e.g., mountains, ocean basins). Plate Tectonics: interaction of moving lithospheric plates – results in major structural features of the Earth. A unifying theory in geology that explains a wide range of geologic phenomena. What did the modern theory replace? Diastrophism: early term for all movement of the Earth’s crust. •Thought to result in formation of mountains, ocean basins, etc. Contracting Earth Theory: Earth contracted or shrank over geologic time. Earth shrank – diameter was smaller but circumference was the same – resulted in folding and buckling of the crust Contracting Earth Theory: Widely accepted but a scientific house of cards. Continental Drift First evidence: jigsaw puzzle fit of outline of continental margins. Frances Bacon (1620): noticed that outlines of S. America and Africa would fit together “jigsaw puzzle” fit is best when the outline used is the edges of the continental shelves. Frances Placet (1668) – first to suggest that continents were once fixed together Alfred Wegener “father of continental drift” found lots of evidence that continents moved over time. In 1915 Wegener published his work in The Origin of the Continents and Oceans. Wegener’s Evidence: Fossils on separate continents Cynognathus Mesosaurus Lystrosaurus Glossopteris How did they get from continent to continent? Paleoclimate evidence Ancient glaciers, deserts, and reefs In the modern world glaciers are found near the north and south poles. Deserts are largely found in bands that are parallel to the equator. Extensive reef complexes lie along the equator, with Tropical regions developing between the reefs and deserts. Desert deposits and reefs that are several hundred million years old are found in bands that suggest the equator was oriented as shown on the left. If we assume that the poles and equator are fixed, the continents must have been in different positions as shown on the left. The only explanation is that continents used to be somewhere else Glacial deposits, including structures that indicate ice flow direction ∙ located in ancient rocks as shown on the left. Wegener suggested that the pattern formed with continents together at the south pole. Rock Evidence Ancient “cratons” within continents match up when brought together like a jigsaw puzzle. The distribution of mountain belts: not randomly distributed as would be expected for a shrinking Earth. Plus evidence linking Appalachia with the Scotland & Scandinavian mountain chain. Wegener’s Conclusions: 1. Continents were once joined. Therefore, they must have moved apart over time. 2. Contracting Earth theory was not consistent with the facts/evidence. Wegener proposed that continents were pushed by gravity from sun / moon ∙ Ideas strongly challenged by scientists. They suggested ∙ Alternative interpretations of his paleontological data: Rafting Isthmian Links Island Stepping Stones Paleoclimate evidence was explained by movement of the poles rather than the continents. Other evidence was refuted as being “coincidence” or just being incorrect. Errors in Wegener’s data led to easy arguments against some conclusions. • Predicted North America and Europe were moving away from each other at the rate of 250 cm/year……an impossible rate. (we now know they are moving apart at about 3 cm/yr) • Second Biggest problem: mechanism Wegener proposed was impossible and easily demonstrated to be so. The biggest problem was that Wegener’s ideas were contrary to the dogma of the day. •By 1930 there were few geologists who believed Wegener’s hypothesis. •He died while on an expedition to Greenland, two days after his 50th birthday. •Over the next 20 years any suggestion of moving continents was received with strong opposition. •1950s – evidence from geological record of Earth’s magnetic field, and better understanding of structure of ocean floor, began to strongly suggest such movement was possible.