* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Changing Earth
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
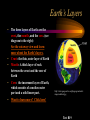
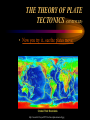
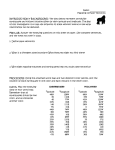
The Changing Earth A Science Lesson for 5th Grade http://www.dc.peachnet.edu/~pgore/students/w97/lehrer/ http://www.geo.utexas.edu/outreach/Barker%20lecture/barker.htm Earth’s Layers • The three layers of Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. (see diagram to the right) See the cutaway view and learn more about the Earth's layers. • Crust: the thin, outer layer of Earth • Mantle: A thick layer of rock between the crust and the core of Earth • Core: the innermost layer of Earth, which consists of a molten outer part and a solid inner part. • Want to learn more? Click here! http://www.geog.ouc.bc.ca/physgeog/contents/i mages/earthcut.jpg Text B19 THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS • Plate Tectonics is the theory of continents drifting from place to place breaking apart, colliding, and grinding against each other • See Pangaea split into the seven continents • Alfred Wegener discovered fossil remains on separate continents that proved the continents were once one giant landmass called PANGAEA • Click on the map for a closer view of the Earth's plates. http://www.exploratorium.edu/faultline/earthquakescience/images/pangea_lrg.gif THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS (CONTINUED) • Now you try it...see the plates move. http://www.lr.k12.nj.us/ETTC/archives/platetectonics2.jpg TECTONIC PLATE MOVEMENT • Plate boundaries are places where plates interact and many earthquakes and volcanoes occur. The three main boundaries are: 1. Convergent boundaries where plates move together 2. Divergent boundaries where plates move away from one another 3. Transform-fault boundaries where plates move past one another http://www.mrd.gov.fj/gfiji/geology/educate/platect.html Mountains • Mountains form as the result of four basic processes: 1. Folding – when masses of rock are squeezed from opposite sides (two plates collide). 2. Faulting – when blocks of rock move up or down along a fault. 3. Doming – when the surface is lifted up by magma. 4. Volcanic Activity http://www.anamericandream.net/testimonials.html Earthquakes • View a globe showing where earthquakes have occurred over a five year period. • Do you have questions about earthquakes? Find the answers here! • See these animated faults in motion! http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/earthq1/san_andreas.gif EARTHQUAKES (CONT.) http://www.ga.gov.au/news/images/GA1117.gif • The instrument used to record the intensity, duration, and nature of earthquake wakes is a seismograph. • The Richter scale is a scale of numbers by which the magnitude of earthquakes is measured. Volcanoes • A volcano is any opening in Earth’s crust through which hot gases, rocks, and melted material erupt. • The melted material that erupts is called magma. • Want to learn more about volcanoes? Click here! http://rwor.org/i/volcano.gif VOLCANOES (CONT.) • A volcano erupts in certain steps: 1. High temperatures and pressures deep within Earth cause rock to melt. 2. Magma makes its way toward the Earth’s surface melting surrounding material to form a central pipe. 3. Hot melted material moves through the volcanic vent. 4. Magma turns to lava. • Watch this animation of a volcanic eruption! http://www.geo.mtu.edu/volcanoes/hazards/primer/image s/volc-images/puuoo.jpg