* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3. Ocean Geography Notes
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Paleoflooding wikipedia , lookup
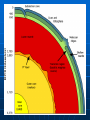
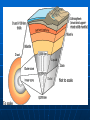
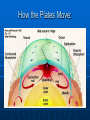
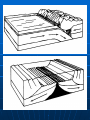
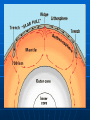
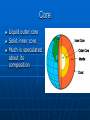
Ocean Geography 1. Earth’s Interior Interior of the Earth: Three main levels: • Crust • Mantle • Core Volume Distribution: • Core – 15% • Mantle – 85% • Crust - >1% Density increasing Crust Since it is the only accessible layer, we know the most about it. Consists of layered rocks located on 12 plates The MOHO separates the crust from the mantle Crust slides around on liquid mantle 5 km to 70 km in depth Plates How the Plates Move: Sea Floor Spreading: Two types of crust, Continental & Oceanic Oceanic crust is constantly being reformed When it meets the continental crust it subducts into the mantle because it is more dense Mantle: Heat from the core drives the convection in the mantle which in turn drives plate tectonics Makes up the majority of the Earth’s volume Solid, though ductile enough it flows on a long enough period of time Core Liquid outer core Solid inner core Much is speculated about its composition Ocean Geography 2. Ocean Floor Features Ocean Floor Features Continental Shelf – Shallow, sloping region that extends beyond the continent Continental Slope – Steep drop off located at the end of the continental shelf Ocean Floor Features Abyss – deeper regions of the ocean Abyssal Plain – nearly flat, smooth region of the ocean floor Ocean Floor Features: Mid Ocean Ridge – Mountain range in the ocean created usually by diverging or converging plates Trench – deep steep side Canyons Ocean Geography: 3. Land & Water Features Bay A body of water surrounded on three sides by land Strait/Sound Water passage that connects two bodies of water or water ways Delta A landform created from the deposits of a river as it enters a sea or ocean Sea Usually a large body of salty water connected to an ocean Cape A long pointed piece of land that sticks out into an ocean, lake, or sea Peninsula A piece of land surrounded on three sides by water Lake Body of water surrounded on all sides by land, very large ones are sometimes called seas Fjord Long narrow sea inlet border on the sides by steep cliffs