* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.4 Powerpoint
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
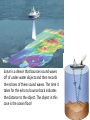
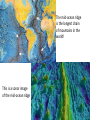
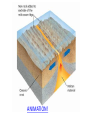
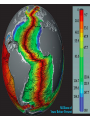
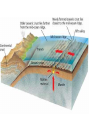
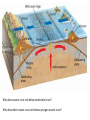
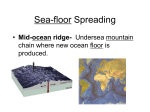
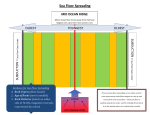
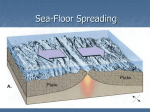
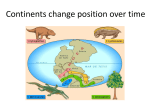
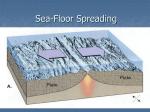
1.4 Sea-floor Spreading Check your notes for key ideas! 1. Mid-Ocean Ridges • An underwater mountain range stretching all over Earth. • Scientists used sonar to map the ocean floor • Mapping the mid-ocean ridge made scientists more curious about what is happening on our ocean floor! Sonar is a device that bounces sound waves off of under-water objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The time it takes for the echo to bounce back indicates the distance to the object. The object in this case is the ocean floor! The mid-ocean ridge is the longest chain of mountains in the world! This is a sonar image of the mid-ocean ridge 2. What is Sea-Floor Spreading • Harry Hess, and American geologist, studied midocean ridges and developed the idea of sea-floor spreading. – Sea-floor spreading: process by which new rock is continuously added to the sea-floor IDEA: – At mid-ocean ridges, molten material pushes up through cracks in the crust. – The new rock pushes old rock away from the ridge. – The ocean floor moves like a conveyor belt and carries the continents with it! (ALFRED WEGENER was on to something!) ANIMATION! 3. Evidence for sea-floor spreading A. Evidence from Molten Material – Scientists dive to ocean floor in submarine, Alvin – Find rocks shaped like pillows. This rock shows that molten material has erupted again and again along the mid-ocean ridge 3. Evidence for sea-floor spreading B. Evidence from Magnetic Stripes – As the rock cools, it becomes magnetized parallel to Earth’s magnetic field at the time. – Earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times. – Scientist discover that the rock making up the ocean floor lies in a pattern. • Reversed; Normal; reversed; Normal – This pattern is the same on each side of the midocean ridge, which suggests it is spreading from both sides! ANIMATION! VIDEO! 3. Evidence for sea-floor spreading C. Evidence from Drilling Samples – Glomar Challenger gathered drill samples – Determine age of rocks Findings: • Rock closer to the mid-ocean ridge is younger. • Rock farther away from midocean ridge is older. The old rock has moved away from the ridge. 4. Subduction at Trenches • Deep-ocean trenches are underwater canyons. • At these trenches, OLD ocean floor bends down and sinks back into the mantle. • Subduction is the process by which the ocean floor sinks. • It takes rock about 200 million years to go from the mid-ocean ridge to the deep ocean trench. Why does oceanic crust sink below continental crust? Why does older oceanic crust sink below younger oceanic crust? Mid-Ocean Ridge: New rock surfaces Magma rises through cracks in crust Rock becomes magma in asthenosphere. Old rock pushed aside Deep Ocean Trenches: Old rock sinks into mantle • Pacific Ocean: – Shrinking. – Old crust is subducting faster than new crust is being made. • Atlantic Ocean: – Expanding. – Lots of new rock forming and very little place for old rock to go. – Connected to continents. As it spreads, it moves the continents and gets wider