* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sea Floor Spreading NOTES 2016 Key
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
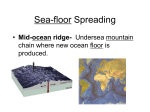
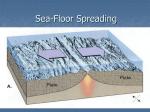
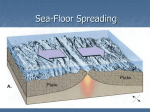
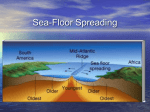
NAME: __________________________________________ CLASS PERIOD: 2 3 4 5 6 SEA FLOOR SPREADING Sea-floor _spreading__ is a process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor. It is the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies. Spreading Process 1. Starts at the __mid-ocean ridge___ 2. Molten material rises from the ___asthenosphere____ and erupts. 3. The molten material then ______spreads out_______ 4. Pushes ___older___ rock to both sides of the ridge. 5. The molten material ___cools___ 6. Forms a strip of solid rock in the center of the ridge. 7. More molten material splits apart the strip of solid rock. 8. ___Pushes____ it aside. 9. The process starts over again. Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading 1. Magnetic ___Reversals_____: Throughout Earth’s history, the north and south magnetic poles have changed places many times. When the poles change places, the ___polarity__ of Earth’s magnetic poles changes ____Molten___ rock at mid-ocean ridges contains tiny mineral grains of __iron__. These minerals align with Earth’s magnetic field. When molten rock cools, the minerals solidify in place and record information about the polarity of the Earth during a certain period of time. If the magnetic field changes, the grains will align in the __opposite___ direction. 2. Mid-Ocean Ridge: The longest chain of __mountains___ in the world Discovered using a ___sonar__ which is a device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects, and then records the echoes of these sound waves. Curves along the sea floor, extending into __all_ of the Earth’s oceans. If seafloor spreading DID NOT occur, the ocean floor would be __flat___. 3. Rocks shaped like _pillows__ that can only form if molten material hardens quickly after erupting under water have been found in the central valley of the mid-ocean ridge. 4. Scientists took samples of rocks for testing. Rocks __farther__ away from the ridge were older than the ones __closest___ to the ridge. NAME: __________________________________________ CLASS PERIOD: 2 3 4 5 6 If seafloor spreading DID NOT occur, all of the oceanic crust would be the ___same___ ___age__. Does the ocean floor just continue to get bigger and bigger? NO! The ocean floor sinks beneath deep underwater canyons called deep-ocean __trench___ Where there are trenches, __subduction___ takes place. Subduction is the process by which the ocean floor __sinks___beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle. Fun Facts These processes cause the ocean floor to be renewed about every _____200 million___ years. The ___Pacific__ Ocean is shrinking – the trenches are swallowing more ocean crust than the mid-ocean ridge is producing. The ___Atlantic___ Ocean is expanding – in most places the oceanic crust is attached to the continental crust. Which two boundary types balance each other? A ___divergent__ boundary, which __creates__ new crust, and a __convergent__ boundary, which ___destroys__crust.