* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ecosystem
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
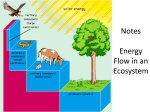
Ecosystems • An ecosystem includes all of the organisms as well as the nonliving things in a given area. Ecosystem Ecosystem Community Community Population Population Organism Organism • A community is a group of different species that live together in one area. Community Community Population Population Organism Organism An ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic factors. Biotic factors are living things. plants animals fungi bacteria plants Abiotic – – – – – factors are nonliving things. moisture temperature wind sunlight soil sunlight moisture What is the primary source of energy for an ecosystem? Producers Makes food by changing light energy of the sun into chemical energy, or food Also called Autotrophs Ex. Plants, algae, some bacteria Consumers Organisms own food Also Ex. that do not make their known as HETEROTROPHS Rabbits, Deer, Mushrooms Heterotrophs Heterotrophs Consumers A. Herbivores – eat ONLY plants Ex. – Cows, Elephants, Giraffes Heterotrophs Consumers B. Omnivores – eat BOTH plants and animals Ex. – Bears and Humans Heterotrophs Consumers C. Carnivores – eat ONLY other animals Ex. – Lions, Tigers, Hawks Heterotrophs Consumers D. Scavengers/Detritivores – feed on the tissue of dead organisms (both plants and animals) Ex. – Vultures, Crows, and Shrimp Heterotrophs Consumers E. Decomposers – absorb any dead material and break it down into simple nutrients or fertilizers Ex. – Bacteria and Mushrooms Food Chain Food Chains The energy flow from one trophic level to the other is know as a food chain Producers are at the first TROPHIC LEVEL Primary Consumers are the SECOND TROPHIC LEVEL Secondary consumers are at the THIRD TROPHIC LEVEL Trophic Levels (feeding levels) 3 2 1 Food Web Most organisms eat more than JUST one organism When more organisms are involved it is know as a FOOD WEB Food webs are more complex and involve lots of organisms Food webs Trophic Level ( Energy Producer, primary Pyramid level) consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer? Grass Mouse Grasshopper Frog Owl Hawk Trophic Level Producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer Producer Grass 1st Mouse 2nd Primary consumer Grasshopper 2nd Primary consumer Frog 3rd Secondary consumer Owl 3rd and 4th Hawk 3rd Secondary and tertiary consumer Secondary consumer Transfer of Energy When a lion eats a zebra, it does not get all of the energy from the zebra (much of it is lost as heat) Only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next – this is called the 10% rule Ecological Pyramid Three hundred trout are needed to support one man for a year. The trout, in turn, must consume 90,000 frogs, that must consume 27 million grasshoppers that live off of 1,000 tons of grass. -- G. Tyler Miller, Jr., American Chemist (1971) Energy Pyramid • • • • • Which level has the most energy? Which level has the most organisms? Which level has the least organisms? Which level has the least energy? Classify the organisms according to their role in a food web. Pyramid of Numbers • Shows the numbers of individual organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem. tertiary consumers 5 secondary consumers 5000 primary consumers 500,000 producers producers 5,000,000 • A vast number of producers are required to support even a few top level consumers. Biomass pyramid • Biomass is a measure of the total dry mass of organisms in a given area. tertiary consumers 75 g/m2 150g/m2 secondary consumers primary consumers producers producers 675g/m2 2000g/m2