* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bacteria - Cloudfront.net
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
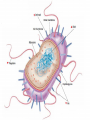
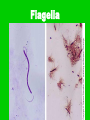
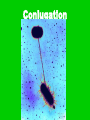
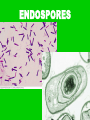
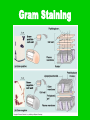
BACTERIA • Bacteria on the tip of a pin! Composed of • One, circular chromosome • Plasma membrane • Ribosomes • Cell wall with peptidoglycan Composed of • Some have – Capsule • Slimy outer layer – Flagella – Pili • Straw-like extensions • Allow bacteria to stick to host • Some allow conjugation – Exchange of plasmids Flagella Conjugation Composed of • Some have –Plasmids •Only in some bacteria •Tiny circles of DNA •Only a few genes PROKARYOTIC • No membrane-bound organelles • Smaller than eukaryotes • All unicellular Reproduction • Binary Fission –Chromosome is replicated –Cell elongates and then splits in two –NO MITOSIS NECESSARY METABOLISM • Some heterotrophic • Some autotrophic –Photosynthesizers –Chemosynthesizers •Can get energy from nonorganic compounds: • ex H2S, NH3 METABOLISM • Some Aerobic – Require O2 • Some Anaerobic – Obligate anaerobes •Killed by O2 – Facultative anaerobes •Can exist with or without O2 METABOLISM • Some secrete TOXINS –Chemicals that are poisonous to eukaryotic cells –Ex: Tetanus, botulism COLONIES • Large clumps of thousands of bacteria all grown from one ancestor • Are genetically identical • Each species has colonies with particular characteristics such as color, shape, texture COLONIES BACTERIAL SHAPES • Coccus – Round • Bacillus – Rod-shaped • Spirillum – Spiral-shaped • Vibrio – comma-shaped Vibrio GROUPINGS • Micro – individual • Diplo – pairs • Strepto – chains • Staphylo - clusters Diplococcus Staphylococcus Streptococcus Streptomyces ENDOSPORES • Hard-shelled case built around DNA during harsh conditions ENDOSPORES Gram Staining • Gram Positive – Blue –No capsule • Gram Negative –Red –Capsule Gram Staining Gram Staining • Helps doctor decide which antibiotic to use Uses of Bacteria • Ecosystems – Decomposers – Nitrogen fixation – Oil eaters • Foods – Chocolate, soy sauce, yogurt, vinegar Uses of Bacteria • Antibiotics and other chemicals • Genetic Engineering –Plasmids used to introduce genes –Insulin, growth hormone Antibiotics • Interfere with bacterial metabolism • Are not effective against viruses • Used to treat bacterial diseases • Penicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, sulfa drugs, cephalosporins, etc. Vaccinations • Small amount of inactivated virus or bacteria injected or ingested • Immune system mounts longlasting response • Prevents rather than treats disease • Measles, mumps, rubella, polio, chicken pox, meningitis, HPV, hepatitis, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus