* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virus - WordPress.com
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
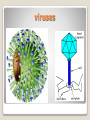
Viruses What are viruses? A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms Viruses are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Viruses are parasites. They can't multiply on their own, so they have to invade a 'host' cell and take over its machinery in order to be able to make more virus particles. viruses Spread of Viral & Bacterial Diseases Viral and bacterial infections are both spread in basically the same ways. A person with a cold can spread the infection by coughing and/or sneezing. Bacteria or viruses can be passed on by touching or shaking hands with another person. Touching food with dirty hands will also allow viruses or bacteria from the intestine to spread. Illnesses/infections caused by Viruses: Chicken pox, influenza, common cold, flu, ear infections, measles, polio, HIV/AIDS, dengue How to avoid infection Wash your hands Shaking hands with someone who has a cold is risky, so avoid rubbing your eyes or nose afterwards. Food should be cooked or cooled down as quickly as possible. Vegetables and meat must be stored separately and prepared on separate chopping boards.