* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download VIRUSES AND BACTERIA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
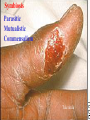
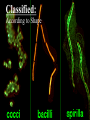
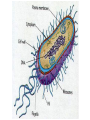
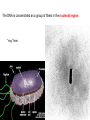
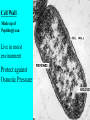
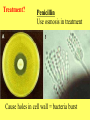
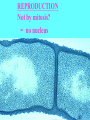
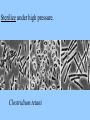
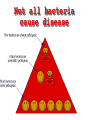
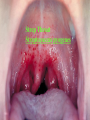
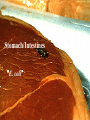
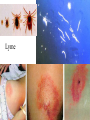
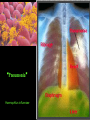
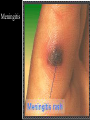
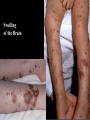
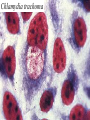
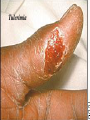
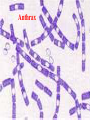
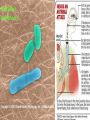
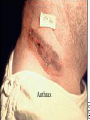
CHAPTER 19 VIRUSES AND BACTERIA BACTERIA Most ancient life form = 3.5 billion years old Smallest and simplest free-living organism Major Role? Saprobes: Decomposers (recycle nutrients) 2 Different Kingdoms: Archaebacteria Eubacteria Archaebacteria: Live in extreme environments “Extremophiles” Methanogens = Anaerobic Methane Sulfur Springs Yellowstone NP “Thermophiles” Methanococcus jannischiiwas 2600 meter in Atlantic Ocean Halophiles Salt Loving Dead Sea Eubacteria: Wide variety Where Found? Everywhere 40,000 Metabolic Diversity Autotrophic Heterotrophic Photosynthetic Chemosynthetic: Break down inorganic substances Nitrogen Fixation Rhizobium Symbiosis Parasitic Mutualistic Commensalism Tulerimia Classified: According to Shape Cocci = Round Streptococcus Bacilli = Rod “Link Sausage” Bacillus anthracis Spirilla = Spiral Coccus = single Strepto = chains Staphylo = clusters Diplo = pairs PREFIX STRUCTURE The DNA is concentrated as a group of fibers in the nucleoid region “ring” form Cell Wall Made up of Peptidoglycan Live in moist environment Protect against Osmotic Pressure Treatment? Penicillin Use osmosis in treatment Cause holes in cell wall = bacteria burst Not effective against viruses and animal cells? None toxic to plants? peptidoglycan REPRODUCTION Not by mitosis? = no nucleus Binary Fission Asexual Identical Cells? 20 minutes Temperature Dependent Bacteria Reproduction Temperature Bacteria Doubles 90º F Every 1/2 Hour 70º F Every 1 Hour 60º F 50º F 40º F Every 2 Hours Every 3 Hours Every 6 Hours 36º F 32º F Every 12 Hours Every 20 Hours Source: Iowa State Journal of Science - 1959 Bacteria Count/sq. cm. on Chicken in a 40º F Cooler TIME # of BACTERIA CONDITION Day 0 360 OK Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 5,800 92,000 1,475,000 OK OK OK-Odors Day 4 Day 5 23,600,000 377,500,000 Off Odors Slime Source: Iowa State Journal of Science - 1959 WHY SO SUCCESSFUL? Reproduction Antibiotics “Mutations” Endospore (around DNA) -Bad conditions Resistant to drying out, boiling, chemicals 1000’s of years Clostridium botulinum Sterilize under high pressure. Clostridium tetani BACTERIAL EFFECTS? Nitrogen Fixation -helps plants Aquaspirillum annulus Escherichia coli “E. coli” Flavors: Vinegar Yogurt Butter Cheese Pickles Sauerkraut “Nonbiodegradable” Sewage “Bioremediation” BAD “Germs” Passed by hands “Antibacterial” Soap Cuts “Infected” “Boil” “Abscess” Hair Follicle Mouth Entamoeba gingivalis Strep Throat Streptococcus pyogenes Stomach/Intestines “E. coli” Helicobacter pylori Intestinal Lyme Streptococcus “Pneumonia” Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis Swelling of the Brain STD’s? Most common STD Chlamydia trachoma Gonorrhea Neiserria gonorrhoeae Same symptoms/ effects Syphilis Treponema pallidum BIOLOGICAL WARFARE Tulerimia Bubonic Plague Anthrax Bacillus anthracis Anthrax Anthrax Bubonic Plague Ebola Smallpox END