* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibacterials ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
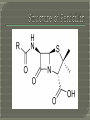
What keeps us away from bacteria! Antibacterial: Chemicals which prevent the growth and multiplication of bacteria Antibiotics: Chemicals produced by micro-organisms that act against other micro-organisms. The “magic bullet” introduced by German Scientist Paul Ehrlich, was a chemical designed to attack pathogenic cells without destroying the host cell. This concept was used to treat syphilis In the 1890’s Scientists discovered that some kinds of fungi could in fact kill bacteria 1928, discovered that a mold on a Petri dish inhibited bacterial growth, he incurred that the mold had produced a compound which he called Penicillin. This discovery was not pursued by Flemming. They isolated the antibacterial that was produced by the mold. Chain also worked out how to concentrate and isolate the Penicillin alone. Using corn-steep liquor Florey and Chain produced the Penicillin in bulk, revolutionizing medical world. Industrialized in America in 1944 antibacterial’s reduced the death tolls. Reducing the death toll during the second world war Penicillin became largely advertised First of there are two types of bacteria. Gram Gram Positive: Simple cell wall Negative: Complex cell wall with many layers difficult to penetrate Three simple steps. 1. Prevents the cell wall formation 2. Water then enters the cell (bacteria walls) 3. The bacteria is destroyed Different Penicillin's work under different environments. The R chain on the Pencillen structure is what's modified in order to gain different benefits. Two types of antibiotics Broad spectrum: effective against a wide range of bacteria including beneficial bacteria. Blood/Urine test not required. Can be bought over counter Narrow spectrum: effective against certain types of bacteria leaving others unharmed, blood and urine tests determine which bacteria in order to gain a viable prescription. Like most topics in chemistry there are exceptions to Penicillin. The more Penicillin is used the less effective it becomes hence larger doses are needed. Broad spectrum destroys useful bacteria. Antibacterial drugs are given to animals to prevent diseases, those animals are then passed on to us for human consumption. (causing development of more resistant bacteria) To reduce chances of bacterial resistance other drugs and an important regime is needed. Some people are allergic to penicillin causing skin rash and fever. In more serious cases anaphylactic shock can occur which can be fatal. Medical consent forms are required for penicillin allergic patients.