* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECOLOGY
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
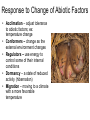
ECOLOGY • Biosphere – Ecosystem •Community – Population » Organism Biosphere the general area of Earth and its atmosphere that supports life About 20 km (13 miles) thick, about 8-10 km (5 - 6 mi) above the Earth’s surface. • Ecosystem: includes all of the organisms and the nonliving environment found in a particular place • Community: is all the interacting organisms in an area; ex: fish, turtles, plants, algae and bacteria in a pond • Population: all the members of a species that live in one place at one time • Organism 2 • Biotic Factors: all living things that affect the organism – Root “bio” means “life” • Abiotic Factors: all nonliving factors … – Prefix “a” means “without” – Includes temperature, humidty, pH, salinity, oxygen concentration, sunlight, nitrogen, and precipitation Response to Change of Abiotic Factors • Acclimation – adjust tolerance to abiotic factors; ex: temperature change • Conformers – change as the external environment changes • Regulators – use energy to control some of their internal conditions • Dormancy – a state of reduced activity (hibernation) • Migration – moving to a climate with a more favorable temperature Energy Transfer • Autotrophs (Producers): create their own food – Include plants and some kinds of protists and bacteria – Use photosynthesis and chemosynthesis • Photosynthesis: conversion of light energy to chemical energy • Chemosynthesis: conversion of energy from chemicals, volcanic vents, etc… Energy Transfer cont. • Heterotrophs (Consumers ): cannot make their own food – Include all animals, most protists, all fungi, and many bacteria – Types include herbivores (plant eaters), carnivores (meat eaters), omnivores (plant and animal eaters), and detritivores (eat dead plants, animals, and animal waste; also called decomposers) Energy Flow • Trophic Level: organism’s position in a sequence of energy transfers • Food chain: a single pathway of feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem that results in energy transfer • Food web: interrelated food chains in an ecosystem Biogeochemical cycles: water carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus Water cycle: movement of water by evaporation, transpiration, and precipitation – Groundwater: water that is in the soil or in underground porous rock – Transpiration: the process by which water evaporates from the leaves of plants Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen fixation: the process of converting N2 gas to nitrate Nitrogen fixing bacteria: transform nitrogen gas into a useable form; grow on the roots of legumes Vocabulary: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism Biotic and Abiotic factors Acclimation Conformers Regulators Dormancy Migration Producers Autotrophs Consumers Heterotrophs Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Detritivores decomposers - trophic level -Food chain -Energy transfer -Biogeochemical cycles -Groundwater -Water cycle -Transpiration -Carbon cycle -Nitrogen cycle -Nitrogen fixation -Nitrogen fixing bacteria