* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gastroenteritis
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
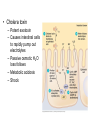
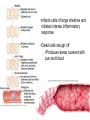
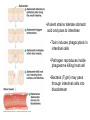
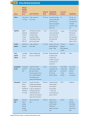
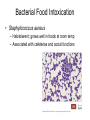
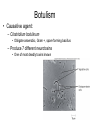
Gastroenteritis • Inflammation of stomach or intestines – Inhibits nutrient absorption and excessive H2O and electrolyte loss • • • • Bacterial Viral Parasites Poisoning by microbial toxins – food borne intoxication • Signs and Symptoms: – General features: diarrhea, loss of appetite, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting and possibly fever – Dysentery – Typically self Limiting • Enteric fevers – Systemic with severe headache, high fever, abscesses, intestinal rupture, shock and death • Epidemiology – Occurs worldwide – Oral to fecal route of transmission • Water common reservoir • Overcrowding & poor sanitation are risk factors • Animals may be source of infection • Prevention – – – – – Hand washing Proper food handling and complete cooking Pasteurization of milk and juices Adequate sanitation Safe water supplies • Treatment – Rapid replacement of fluids and electrolytes – Anti-nausea medication – Antimicrobials may be used in severe cases Bacterial Gastroenteritis • 3 groups of gram negative bacteria account for most bacterial intestinal infections: – Vibrio cholerae (Cholera) – Enterics (Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli) – Campylobacter jejuni Cholera • Causative agent: Vibrio cholerae • High infectious dose – Bacteria sensitive to stomach acid – Adheres to small intestine and multiply – Bacteria don’t enter cells • Cholera toxin – Potent exotoxin – Causes intestinal cells to rapidly pump out electrolytes – Passive osmotic H2O loss follows – Metabolic acidosis – Shock • Heavy loss of fluid – “rice-water stool” • Up to 20L of fluids lost per day • May discharge 1 million bacteria per ml of feces • Untreated cases potentially fatal – Fluid/electrolyte replacement – Tetracycline reduces toxin production Shigellosis • Causative Agent: Shigella sp. – S. dysenteriae, S. flexneri, S. boydii, S. sonnei • Low infecting dose – Bacteria not sensitive to stomach acid – Characterized by fever and dysentery •Infects cells of large intestine and initiates intense inflammatory response •Dead cells slough off •Produces areas covered with pus and blood • All species produce enterotoxin and type III secretion systems • S. dysenteriae produces powerful endotoxin – shiga-toxin • Ciprofloxacin, rifampin or azithromycin may reduce duration and infectivity Traveler’s Diarrhea • Causative Agent: Escherichia coli – Multiple antigenic strains (O, H, K) – Virulent strains have fimbriae, adhesions and multiple toxins • Enterotoxigenic E. coli – Enterotoxins – Type III secretion system – Typically self limiting • Enterohemorrhagic E. coli – O157:H7 – Produce potent Shiga-like toxins and type III secretion systems • Antimicrobials cause increase in toxin production Salmonellosis and Typhoid Fever • Causative agent: Salmonella enterica – 2000 strains (serotypes) – Typhimurium and Enteritidis commonly cause Salmonellosis – Typhi and Paratyphi cause Typhoid Fever • Common intestinal flora of many animals • Contaminated animal products are reservoir • Reptiles, eggs and undercooked poultry •Virulent strains tolerate stomach acid and pass to intestines •Toxin induces phagocytosis in intestinal cells •Pathogen reproduces inside phagosome killing host cell •Bacteria (Typhi) may pass through intestinal cells into bloodstream • Typhoid fever is an enteric fever – Macrophages carry bacteria to liver, spleen, bone marrow and gallbladder – Treated with ciprofloxacin or ampicillin – Surgical removal of gallbladder Campylobacteriosis • Causative agent: Campylobacter jejuni – Leading cause of bacterial diarrhea in United States – Estimated 1million cases annually with ~100 deaths • Associated with poultry – Low infecting dose • Virulent strains possess adhesions, cytotoxins and endotoxin – Induce endocytosis in cells of intestine and initiate inflammation and bleeding lesions • Non-motile mutants are avirulent • Severe cases treated with ciprofloxacin or azithromycin • Guillain-Barré Syndrome – Tingling of the feet leads to progressive paralysis of the legs, arms and rest of the body – 40% of cases preceded by campylobacteriosis – May be associated with autoimmune response – 80% recover completely; 5% mortality with treatment Viral Gastroenteritis • Common causative agents: – Rotaviruses and Noroviruses – Both naked RNA viruses Star-like Noroviruses Wheel -like Rotaviruses • Epidemology – Infect intestinal cells causing cell death – Typically self-limiting – Norovirus epidemics cause 90% of cases – Rotaviruses responsible for 50% infant cases of serious diarrhea • 600,000 worldwide annual fatalities • Oral vaccine available Bacterial Food Intoxication • Staphylococcus aureus – Halotolerent; grows well in foods at room temp – Associated with cafeterias and social functions • 5 heat stable enterotoxins: – 1000 for up to 30 min – Stimulate muscle contractions, nausea and intense vomiting, diarrhea and cramping – Acute and self limiting • symptoms begin 4-6 hrs after consumption and end within 24 hrs Botulism • Causative agent: – Clostridium botulinum • Obligate anaerobic, Gram +, spore forming bacillus – Produce 7 different neurotoxins • One of most deadly toxins known • Signs & Symptoms – Dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision – Abdominal symptoms include pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea or constipation – Progressive paralysis • Paralysis of respiratory muscles most common cause of death • 3 forms of botulism: – Food-borne botulism – progressive paralysis of all voluntary muscles due to toxin production – Wound botulism – similar symptoms – Infant botulism – bacteria grow in the intestines, producing non-specific symptoms • “floppy baby syndrome” • Epidemiology – Food borne botulism • Commercial sterilization • Toxin destroyed by heating foods – Wound botulism • deep crushing wounds – Infant botulism • Inhalation or ingestion of spores • Commonly associated with honey or juices • Prevention – Proper sterilization and sealing of canned food – No honey or unpasteurized juices for infants!! • Treatment – – – – Antitoxin Gastric washing and surgical removal of tissues Artificial respiration may be required Anti-microbials given to kill bacteria in infant and wound botulism