* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
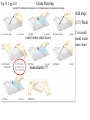
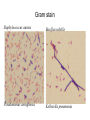
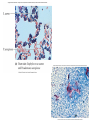
Lab 4 Lab 3 Goals and Objectives • Learn methods of differential staining: – Use two or more stains and categorize cells into groups – Gram Staining – Separates bacteria in two different groups – Gram positive and Gram negative – Important first test for bacterial identification – Acid – Fast Staining – Detects the high mycolic acid content of certain bacterial cell walls, like those of Mycobacteria – Mycolic acids are long fatty acids found in the cell walls of a group of bacteria that includes Mycobacterium tuberculosis. - Important diagnostic tool Gram stain – determine bacterial cell wall structure Figure 15.2 Figure 15.1 GRAM STAIN 1. Crystal Violet = Primary Stain: stains all cell walls purple 2. Iodine = Mordant: combines with crystal violet to create large insoluble dark purple complex 3. Alcohol = Decolorizer: solubilizes Gram negative outer membrane flushing iodine/crystal violet complex out of thin wall, thick Gram positive cells resist decolorization 4. Safranin = Counterstain: stains cell walls pink (obscured by purple walls of Gram positive, but Gram negative, who had become colorless, now are pink) Wax Pencil ***Use wax pencils (China Marker): Sharpie will wash off with alcohol! Be sure to resuspend broth cultures completely! Exercise 15: Gram Stain: Each pair make 2 slides each mix and stain: 1. Staphylococcus aureus & Pseudomonas aeruginosa: two loops of each broth mixed 2 loops each organism mixed together 2. Bacillus subtilis & Escherichia coli: two loops of each broth mixed Fig 15.3 pg 110 Gram Staining Add step: (3.5) Wash 2 seconds (until water runs clear) immediately!!! (until water runs clear) Gram stain Staphylococcus aureus Bacillus subtilis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Kelbsiella pneumonia Exercise 17: Acid Fast Staining 1. Carbolfuchsin – primary stain Staphylococcus aureus 2. Aid-alcohol – decolorizer 3. methylene blue – counter-stain Mycobacterium smegmatis Wax Pencil Each pair make minimum one acid fast slide with: Staphylococcus aureus (use 2-4 loops of broth on slide first) • Mycobacterium smegmatis (slant, use needle, get tiny amount and mix into • broth on slide very well: break up all clumps) 2 loops each organism mixed together Fig 17.1 pg 118 Acid Fast Stain 30sec • ***Make all smears on slides first so they can dry before heat fixing!!! • Split the work to save time but make sure everyone gets to see all slides! • Each pair needs for lab 4: – 1 broth culture Staphylococcus aureus – 1 broth culture Pseudomonas aeruginosa – 1 broth culture Bacillus subtilis (replaces B. megaterium) – 1 broth culture Escherichia coli – 1 wet slant 5 day culture Mycobacterium smegmatis – – – – – – – Crystal violet Gram’s iodine 95% Alcohol (Ethanol) Safranin Methylene blue Acid-alcohol Carbolfuchsin ***95% Ethanol for Gram Stain, Acid-alcohol for Acid Fast Stain!!!