* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
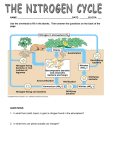
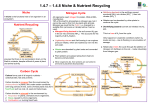
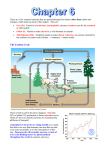
You Need to know 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Definition of Ecology Definition of Biosphere Definition of Ecosystem Definition of Habitat Be able to list 5 types of ecosystems Environmental factors affecting organisms. 1. Abiotic factors are non living factors 2. Biotic factors are living factors 3. Climatic factors refer to weather over a long period of time. 4. Edaphic factors relate to soil (soil pH, soil type, moisture, air and mineral content) Abiotic Factors Steepness Altitude Current Aspect Exposure Steepness and Altitude Currents Biotic Factors Food Competition Predation Parasitism Pollination and seed dispersal Humans Climatic Factors Temperature Rainfall Humidity Day Length Light Intensity Wind Salinity Edaphic Factors Soil pH Organic Matter Water Content Air Content Mineral Content Soil Type Sand Clay Where do we get our energy from? The sun is the primary source of energy for our planet. Feeding allows energy to flow from one organism to another in an ecosystem. Producers are organisms that carry out photosynthesis. Consumers are organisms that take in food from another organism. 3 types of consumers Primary consumers feed on producers Secondary consumers feed on primary consumers Tertiary consumers feed on secondary consumers A grazing food chain is a sequence of organisms in which each one is eaten by the next member in the chain. Grass Rabbit Fox A food web consists of two or more interlinked food chains. Sparrow Hawk Blue Tit Badger Thrush Caterpillar Slug Dock leaves A pyramid of numbers represents the number of organisms at each stage in a food chain. Fox Rabbit Grass Niche The ecological niche of an organism is the functional role it plays in the community. Each bird in the pictures eats and lives in different parts of the habitat and hence do not compete with each other. They have found a niche Can you describe the life of a plant? Nutrient recycling is the way in which elements are exchanged between the living and non-living components of an ecosystem. Elements covered in class are Carbon and Nitrogen Carbon Cycle Carbon dioxide is removed from the environment by: Photosynthesis in plants. Carbon dioxide is returned to the environment by: 1. 2. 3. 4. Respiration in plants, animals & micro-organisms. Decay caused by micro-organisms. Combustion. Weathering. CO2 Levels have increased from 0.028% to 0.036% over 200yrs Main cause is increased combustion of fossil fuels and deforestation Effects of Global Warming 1. 2. 3. Sea levels rise. Weather patterns alter Reverse direction of Gulf Stream Nitrogen cycle All organisms need nitrogen for protein, DNA & RNA 80% of the air is nitrogen gas, (Brilliant I can make as much protein as I want) However…. it is no use to living things as a gas it needs to be changed into a chemical compound called Nitrate NO3 Nitrogen cycle How does the Nitrogen gas change into Nitrate? 1. Volcanic Action 2. Lightning 3. Industrial Processes 4. Some Bacteria Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria N2 gas ammonia(NH3) nitrates(NO3). These bacteria live in the soil or in the roots of clover, beans and peas (Legumes). Plants absorb the nitrates made by the bacteria. In return the bacteria absorbs some of the sugars made by the plant during photosynthesis. Hence the plant and bacteria live in Symbiosis Animals then eat the Plants and get their nitrogen from plant protein. When organisms die they are decomposed by Fungi and bacteria which produce Ammonia. Then more bacteria (called Nitrifying bacteria) change this Ammonia into Nitrate. This process is called Nitrification. Plants can then absorb these nitrates. Then there are other types of bacteria (called denitrifying bacteria) that change nitrates into nitrogen gas. This process is called Denitrification. Human Impact on Ecosystems We are going to look at 3 ways that humans affect ecosystems: 1. Pollution 2. Conservation 3. Waste Management Pollution This is any undesirable change in the environment. Can you name any natural pollutants? Can you name pollution that arises from human activity? Pollution can affect Air, Freshwater, Sea, Soil and Land. Domestic Pollution Agricultural Pollution Industrial Pollution