* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. Kingdoms & Intro to Virus
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
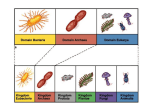
6 Kingdom Classification System Archaebacteria / Eubacteria How we got to the 6 kingdom classification system we have today? 2 Kingdoms Plants and Animals 3 Kingdoms Added Protista (microorganisms) 4 Kingdoms Added Fungi (molds and mushrooms) 5 Kingdoms Added Monera (NO true nucleus) 6 Kingdoms Monera are divided into: Archaebacteria / Eubacteria 2 The 5 Kingdoms Monera - DIVIDED Archaebacteria – thrive in harsh conditions - Cell wall and ribosomes Example: methanogens, thermophiles, halophiles Eubacteria – rigid surface (unusual cell wall) Example: bacteria, cyanobacteria 2.3 5 5/23/2017 Viruses SBI3U - A.Y. Jackson S.S. 5 Questions 1. Where do viruses fit into the model of the 6 Kingdom classification system? 2. Are viruses considered living organisms? 6 6 What are the characteristics of living organisms? 7 Living things… are made of cells grow and develop reproduce respond to their environment adapt to their environment obtain and use energy produce wastes 7 Image of an animal cell cells can fulfill all characteristics of life 8 More realistic size of a virus compared to an animal cell Magnified image of a virus viruses on their own can be considered lifeless chemicals, unless ……? 8 … unless they are reproducing Answer viruses are not considered to be living organisms because: 1. 2. not made up of cells only capable of 1 life function i.e. reproduction & only within a living cell 9 outside cells, viruses are lifeless chemicals 9 capsid: protein coat for protection core: •either DNA or RNA (genetic material) Receptor sites: •spikes that help virus attach to its specific host cell 10 10 Numerous shapes Examples: Rods or filaments: Ebola 11 Tobacco Mosaic Virus 11 Spherical: Influenza SARS HIV Smallpox 12 12 Geometric Shapes: Adenovirus (colds) 20-sided polygon (icosahedron) 13 Bacteriophage T4 Page 104 13 Viruses are generally classified by: 1. 2. 14 the organisms they infect host range (cells that the virus can infect) examples: a) cold virus (human respiratory cells) b) rabies (nerve cells in dogs, rodents, humans) c) HIV (human WBC) d) bacteriophage (bacteria) structure a. size and shape of the capsid b. type genetic material (DNA or RNA) 5/23/2017 14 so small measured in units called nanometres (nm) 1nm = 1X10-9 m (billionth of a metre) 15 size ranges from 20 - 400 nm 5/23/2017 15 5 Kingdom Classification System Organisms Prokaryotes Eukaryotes • very tiny simple cells • no true nucleus • no organelles • larger more complex cells • have a nucleus • have numerous organelles Cell Wall No Cell Wall Autotrophs •make their own food by photosynthesis 1. Monera bacteria Heterotrophs •can’t make their own food •must eat other organisms Unicellular Multicellular 2. Plants 3. Fungi moss ferns yeast mould 4.Protists 5. Animals amoeba *algae insects fish The 5 Kingdoms Some examples of each of the 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria bacteria 2.Archaebacteria methanogens 3. Plants moss ferns 5.Protists 4. Fungi yeast mould mushrooms 18 amoeba *algae 6. Animals insects fish 19 SBI3U - A.Y. Jackson S.S. 5/23/2017