* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria PowerPoint - Effingham County Schools
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
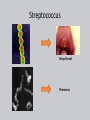
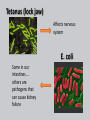
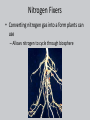
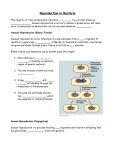
*Growth and Reproduction • *Some bacteria can divide every 20 minutes – If there were unlimited resources, 1 bacteria could grow into a mass 4000 times the mass of earth in just 48 hours!!! What is the role of bacteria in our world? List everything you know Are living: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Made up of cells Have DNA Grow and develop Use energy Homeostasis Reproduction SMART 1) Binary Fission • Binary Fission: – Asexual reproduction where organism replicates DNA and divides in half – Produces two identical daughter cells Reproduction Binary fission 2) Conjugation • Conjugation: (“bacterial sex”) – Sexual reproduction where organism exchange genetic information SMART Come back!!!!! Shapes Cocci Bacilla Spirilla Shapes Streptococus Staphlococus Streptobacilla Staphlobacilla Streptospirilla SSSS S Staphlospirilla Some are BAD and make us ill Streptococcus Strep throat Pnemonia Tetanus (lock jaw) Affects nervous system E. coli Some in our intestines … others are pathogens that can cause kidney failure Bacteria Can be bad … but can be good Feel better with?? Importance of Bacteria Decomposers • Break down things into simpler materials and release into the soil • *Help breakdown sewage treatment water Nitrogen Fixers • Converting nitrogen gas into a form plants can use – Allows nitrogen to cycle through biosphere Other Uses • E. coli in our intestines – Make vitamins that we cannot make • Oil digestion Archaebacteria! Archaea • Lack peptidoglycan walls and have different membrane lipids than Eubacteria • DNA sequences are closer to Eukaryotes than Bacteria Extremophiles • Extremophiles: – Live in extreme environments! Halophilic: salt loving Thermophilic: heat loving