* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 19 – Bacteria Notes
Phage therapy wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Unique properties of hyperthermophilic archaea wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
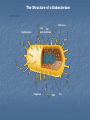
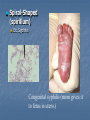
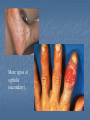
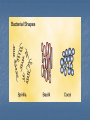
Ch. 19 – Bacteria Notes The Structure of a Eubacterium Section 19-1 Ribosome Peptidoglycan Cell Cell wall membrane Flagellum DNA Pili Review: Kingdom Eubacteria and Archaebacteria; Old Kingdom = Monera Unicellular Prokaryotic, no cellular membranes, no nucleus Auto and Heterotrophic Bacteria Identification: 1. Shape Sphere-Shape (coccus) Ex. Strep Throat (streptococcus), pneumonia (diplococcus), staph (staphylococcus) Rod-Shaped (bacillus) Ex. Typhoid fever (caused by salmonella: Boil it, peel it, cook it, or FORGET IT! Transmitted by ingestion of food or water contaminated with feces of infected people. Typhoid Mary – 36 years quarantined!), Botulism (home canned foods or bad seal on canned foods.) Spiral-Shaped (spirillum) Ex. Syphilis Congenital syphilis (mom gives it to fetus in utero.) More types of syphilis (secondary). More Bacteria Identification: 2. Cell Wall (chemical nature) – can see the wall by gram-staining! 1. 2. Take-up Crystal Violet (purple) = Gram Positive Take-up Safranine (red) = Gram Negative ID Cont. 3. Bacterial Movement 1. 2. 3. Flagella – tail Glide along slime (they make this themselves) Some don’t move! …and the last way to Identify bacteria 4. Oxygen Use 1. 2. Require Oxygen – AEROBIC NO Oxygen ANAEROBIC Growth and Reproduction Bacteria reproduce in three different ways 1. Binary Fission – bacteria double in size, double DNA and divide in half (asexual reproduction) Growth and Reproduction 2. Conjugation – a hollow bridge forms between two bacteria cells and they exchange genetic information (sexual reproduction) Growth and Reproduction 3. Spore formation – when conditions are bad, bacteria form endospores which lay dormant until conditions get better for growth.