* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biofilms role in chronic infections.
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
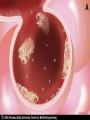
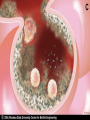
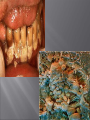
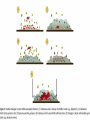
Chad Blankenship Advisor Dr. Bill Grimes Clinical Health Sciences Department University of Kentucky •A biofilm is a community of microorganisms that usually consist of multiple species of bacteria that have the ability to cause chronic pathogenic infections in Humans. Biofilm formation is a crucial step in the pathogenesis of many chronic bacterial infections, including foreign body related infections (Infections on medical devices). Biofilms are very difficult to eradicate with conventional antimicrobial agents so they create huge problems for practitioners in forming treatment modalities that work . Bacterial biofilms have several potential antimicrobial resistance mechanisms. Biofilms form when bacteria adhere to nutrient surfaces in moist environments and begin to excrete a slime layer that can anchor them to all kinds of material – such as metals, plastics, biomedical implants , and human tissue. •Contact lenses •Central venous catheters •Endotracheal tubes •Intrauterine devices •Mechanical heart valves •Pacemakers •Dialysis catheters •Urinary catheters •Voice protheses Nutrient acquisition Protection •Restricted Penetration •Decreased growth rate •Expression of resistance genes I just can't go with the flow anymore. I've been thinking about joining a biofilm. •Persister cells http://www.erc.montana.edu/Res-Lib99SW/Movies/2005/05-M005.htm •Plaque •Infectious Bacterial Endocarditis •Urinary tract infections •Cystic Fibrosis •Tuberculosis •MRSA Tuberculosis is a very relevant very contagious pulmonary disease that is spread by direct contact with respiratory droplets. It is estimated that 1.6 million deaths resulted from TB in 2005 • Researchers have discovered that mycobacteria, the etiologic agent of tuberculosis, has the ability to form biofilms (Howard Hughes 2005). The ability to form biofilms as discussed allows these infections to persist causing chronic infections that are not easily cured. It has been found however that when mycobacterium species related to TB pathogens lack one key protein, mature biofilms fail to form. Corrupting this protein inactivates a key gene (GroEL1) which prevents biofilm formation and takes away the ability of the bacteria to evade antimicrobial penetration (Howard Hughes 2005). GroEL1 apparently oversees the production of fatty acids called mycolic acids that help in the production of mature biofilms. So, If we take away the biofilms ability to protect the bacterial community we can then use the traditional treatments in order to clear these infections. One in 3,000 Caucasian infants is afflicted with this disorder, making Cystic Fibrosis one of the most common genetic diseases, resulting in lethality, in Caucasians. This means there are approximately 30,000 Americans with CF, and an estimated 8 million people who are heterozygous for the defective gene that causes the disease. • Cystic Fibrosis is caused by infection of the alveoli of the lungs with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The alveoli slowly fill with mucous and damage is caused to the lung tissue which cause labored breathing and eventually death. Cystic Fibrosis is now believed to form biofilms in the alveoli from neutrophils. The infection is continually challenged by the immune system with an endless supply of neutrophils. The neutrophils themselves increase the amount of debris that clog the alveoli of the lungs. Scientists have found that the DNA and a filament by the name of actin, develop the structure the Pseudomonads need to from mature biofilms. In the presence of these neutophils, Pseudomonas is three times more likely to form biofilms than if neutrophils were not present. These biofilms give the pseudomonas increased protection from assault by macrophages or neutrophils that may try to penetrate the infection. Periodontitis is an infection of the soft tissue surrounding the teeth which is set into motion by the substance known as plaque. Plaque is the combination of bacteria and food particulate mixed with salivary secretions. It is widely known that plaque is an active biofilm. Plague can advance to calculus which is tarter found on the teeth. More than one in three people over age 30 have Periodontitis. And, by a conservative estimate, 35.7 million people in the United States have Periodontitis (Albandar 1999). • is the inflammation of the endocardium or inner layer of the heart. The most common structures that become involved in this inflammation are the four heart valves themselves. In a paper by Braunwald he suggests that the percentages of bacterial infection for all popularly used prosthetic heart valve remain in the same range of .5% - 4%. However when these heart valves begin to leak they form biofilms easily. The biofilms can break away and get clogged in capillary beds causing embolisms. • In the past few years the amount of MRSA infections has gone up considerably. A 2007 report in Emerging Infectious Diseases, (CDC), estimated the number of MRSA infections doubled nationwide, from approximately 127,000 in 1999 to 278,000 in 2005, while deaths increased from 11,000 to 17,000. JAMA estimated that MRSA was responsible for 94,360 serious infections and associated with 18,650 hospital deaths in the United States in 2005. If the estimations are fair, reports Rob Stein of the Washington Post, then MRSA is responsible for more deaths each year than AIDS. • In a study by F. Fitzpatrick et al in 2005 it was found that isolates of MRSA contained the ica operon that makes it possible for them to form biofilms while isolates of MSSA (multi-strain susceptible staphylococcus aureus) did not contain the ica operon and are as the name suggested more susceptible to antimicrobial penetration. This research suggests that biofilm formation is a important catalyst for resistance in MRSA. Methicillin resistance coupled with the ability to form biofilms is bad news for future treatment efforts. The more we understand about biofilm formation the more likely we are to find a treatment. There are not many answers about how to treat chronic infections caused by biofilm formation!!! However, this is something that researchers predict will trickle down into the medical field in yrs to come.