* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibody specificity - Union County College Faculty Web Site
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
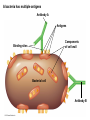
Antibody specificity 1. Bind to a very specific molecule 2. The molecule they bind to is an antigen 3. Antibodies will be made against virtually any molecule, even molecules that have never existed Antibody generation 1. At birth, you have genes coding for thousands of antibodies. 2. These will bind weakly to most antigens. 3. Following weak binding, antibodies are modified randomly, until more strongly binding antibodies are produced. This process is call affinity maturation Antibody structure 1. Y- shaped, with 2 binding sites 2. Therefore can aggregate cells, viruses, or other structures with more than one copy of an antigen 3. Antibodies have a variable region and a constant region. The binding sites are in the variable region. A bacteria has multiple antigens Antibody A Antigens Components of cell wall Binding sites Bacterial cell Antibody B Antibody subclasses • • • • • IgG – most abundant IgM – “immature” Ab, lower affinity IgA – in secretions IgE – responsible for allergies IgD Lymphocytes 1. There are 2 major types of lyphocytes: B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes 2. B lymphocytes make antibodies 3. T lymphocytes have Ab-like molecules on their cell membrane, which are the T-cell receptors