* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20.1 viruses wkbk key - OG
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
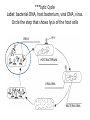
Viruses Wkbk 20.1 Watch for vocab, diagrams, and understanding structure and function of viruses The Discovery of Viruses *1. What is a bacteriophage? Virus that attacks bacteria *2. What are viruses? Particles of nucleic acid, protein, and lipids that reproduce only by infecting living cells *3. What is a capsid? Protein coat on a virus (for protection) 4. How does a typical virus get inside a cell? Capsid proteins “trick” the cell by binding to its receptors 5. What occurs when viruses get inside cells? Virus genes (DNA) are expressed; may lead to cell’s destruction Viral Infections 6. Visual Analogy: Why is the outlaw locking up the sheriff, instead of the other way around? Virus = outlaw that takes hostage of the cell Cell = sheriff (no longer in control) ***Lytic Cycle Label: bacterial DNA, host bacterium, viral DNA, virus. Circle the step that shows lysis of the host cells VIRUS HOST BACTERIUM VIRAL DNA BACTERIAL DNA Viral Infections Cont’d 8. In a lysogenic infection, how can one virus infect many cells? Virus DNA is copied into cell’s DNA, and it gets multiplied every time the cell multiplies 9. How is the common cold like HIV? Both are RNA viruses *10. What would happen to a virus that never came in contact with a living cell? Explain your answer. It would never reproduce, just sit there waiting. Cannot do ANYTHING without a host – can’t move by itself either Compare Virus vs. Cell