* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Peopling of the World
Agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Hunter-gatherer wikipedia , lookup
Civilization wikipedia , lookup
Nutritional anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary origin of religions wikipedia , lookup
Three-age system wikipedia , lookup
Post-excavation analysis wikipedia , lookup
Early human migrations wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
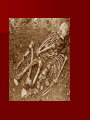
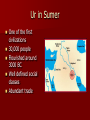
The Peopling of the World Chapter 1 How do we study life before the invention of writing? Main Ideas Interaction with the Environment – As humans spread out over the world, they adapted to each environment they encountered Science and Technology – The earliest peoples came up with new ideas and inventions in order to survive Economics – Early humans hunted and gathered wild plant foods for 3-4 million years. About 1,000 years ago they learned to tame animals and plant crops Human Origins in Africa Main Idea Fossil evidence shows that the earliest humans originated in Africa in the Great Rift Valley and spread across the globe Search for Human Origins Archaeology Archaeologists work like detectives to uncover the story of prehistoric peoples They learn about early people by excavating and studying the traces of early settlements Archaeology Archaeologists analyze evidence such as bones and artifacts- human made objects such as jewelry and tools What kinds of things can archaeologists learn from studying bones and artifacts? Archaeology Bones What people looked like How tall they were How they died Diseases they had Food they ate How long they lived Artifacts How people dressed How people worshipped Clothes they wore Anthropology Anthropologists study culture Culture- people’s unique way of life They use artifacts to recreate a picture of early people’s cultural behaviors Elements of culture – Paleontology Paleontologists study fossils Early Footprints Found In 1978, archaeologist Mary Leakey led an expedition in Tanzania, Africa where they found footprints of a hominid –creatures that walk upright Believed to be 3.6 million years old Lucy 1974, anthropologist found the skeleton of a hominid in Ethiopia 3.5 million years old Australopithecines Walked upright – Easier to spot threats – Easier to carry children and food – Travel distances more easily Had opposable thumbs – Able to pick up small objects and make tools Stone Age 2 parts Paleolithic Age – 2.5 million to 8000 BC – Stone tools Neolithic Age – 8000 BC to 3000 BC – Polish stone tools, make pottery, grow crops, and raise animals Homo habilis Man of skill East Africa 2.5 million years ago Believed to have used tools for cutting meat and cracking open bones Homo erectus Upright man 1.6 million years ago More intelligent and adaptable Developed technology- ways of applying knowledge, tools, and inventions to meet their needs Skillful hunters First hominids to migrate from Africa First to use fire May have developed spoken language Dawn of Modern Humans Homo sapiens – species name for modern humans, “wise men” Much larger brains First believed that Neanderthals and CroMagnons were traditionally classified as early groups of homo sapiens Proven that Neanderthals were not related but may have competed with Cro-Magnons for land and food Neanderthals Slanted brows, well developed muscles, thick bones Tried to explain and control their world Developed religious beliefs and performed rituals Used caves or temporary shelters to survive the harsh winters Cro-Magnons About 40,000 years ago Skeletal remains are identical to humans Strong and about 5 ½ feet tall Planned hunts, stalked prey Advanced skills in spoken language New Findings Ape-like fossils recently discovered in Chad and Kenya date back 6 to 7 million years May be the earliest hominids Researchers in 1996 discovered a Neanderthal bone flute – suggests they had musical expression Humans Try to Control Nature Main Idea Development of agriculture caused an increase in population and the growth of a settled way of life Early Advances in Technology and Art For thousands of years people were nomads – people who moved from place to place foraging for food Hunter-gatherers – groups whose foods supply depends on hunting animals and collecting plant foods Tools- Cro-Magnons used tools like spears and digging sticks to increase their food supply Artistic Expression in the Paleolithic Age Necklaces of seashells, lion teeth, bear claws Beads from mammoth tusks Small sculptures of animals Cave paintings exist all over the world Beginnings of Agriculture About 10,000 years ago Neolithic Revolution – agricultural revolution Shift from food gathering to food producing What are the causes of the Neolithic Revolution? Causes of Neolithic Revolution Change in climate Rising temperatures allowed for longer growing seasons Rich supply of grain led to population increase Farming provided a steady food source for new larger populations Early Farming Methods Slash and burn – cut trees or grasses and burn them to clear a field Ashes provide fertilizer Farmers plant for a year or two then move on Domestication of Animals Domestication – taming Horses, dogs, pigs, and goats Slow process from hunting animals to driving them into enclosures and taming them Villages Grow and Prosper Agriculture allowed people to settle in one place and develop villages Benefits-allowed for support of skilled workers such as weavers and potters Drawbacks- fire, disease, floods, drought, enemies Civilization Main Idea Prosperous farming villages, food surpluses, and new technology led to the rise of civilizations Villages Grow into Cities As people developed better technology to control their environment they reaped larger harvests Settlements with plentiful food supplies could support larger populations Economic Changes Food surpluses freed some villagers to pursue jobs other than farming and develop new skills Craftspeople created valuable new products such as pottery, metal objects, and woven cloth People also began to trade goods with each other Helped by the invention of the wheel and the sail Social Changes Social classes began to emerge as cities grew People now had different jobs and varying levels of wealth and power Religion became more organized – Common spiritual values became lasting traditions What are the characteristics of a civilization? How civilization develops Civilization- complex culture with 5 characteristics 1. advanced cities 2. specialized workers 3. complex institutions 4. record keeping 5. advanced technology Advanced Cities Birthplaces of the first civilizations Center of trade for a larger area Specialized Workers Specialization- development of skills in a specific kind of work Artisans – skilled workers who make goods by hand Food surpluses allowed people to become experts at one job Complex Institutions Institutions- long-lasting pattern of organization in a community Government, religion, economy Record keeping Record keeping became more necessary as institutions became more complex Tax collection, laws, storage of grain Calendar for religious rituals Debts and payments Scribes- professional record keepers Cuneiform- early system of writing invented in Sumer Soon began writing about things other than records such as dramatic events Improved Technology Needed to solve problems that arose when large groups of people live together Using animals to pull plows Irrigation to water fields Potter’s wheel Bronze Age- when people began using bronze rather than copper or stone Began around 3000 BC Ur in Sumer One of the first civilizations 30,000 people Flourished around 3000 BC Well defined social classes Abundant trade What was the Neolithic Revolution and why was it important?