* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit – iv
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
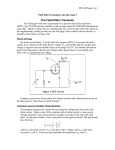
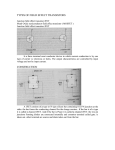
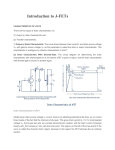
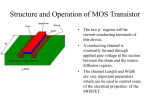
Unit – iv TYPES OF FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS Junction field effect transistor JFET Metal Oxide semiconductor field effect transistor ( MOSFET ) Junction field effect transistor JFET Is a three terminal semi conductor device in which current conduction is by one type of carrier i.e electrons or holes. The output characteristics are controlled by input voltage and not by input current. CONSTRUCTION A JFET consists of p type or N type silicon bar containing two PN junction at the sides. the bar forms the conducting channel for the charge carriers.. If the bar is of n type it is called n channel JFET. And if the bar is Ptype it is called p channel JFET. the two pn junctions forming diodes are connected internally and common terminal called gate. is taken out. other terminal are source and drain taken out from the bar. WORKING PRINICIPLE When a voltage Vds is applied between drain and source terminals and the voltage on the gate is zero. the two pn junction at the side of the bar establish depletion layers. The electrons will flow from source to drain through a channel between the depletion layers. the size of these layers determined the width of the channel and hence the current conduction through the bar. When a reverse voltage VGS is applied between the Gate and source, width of the depletion layer is increased this reduces width of conducting channel , their by increasing the resistance of n type bar .the current from source to drain is decreased. if the reverse voltage on the gate is decreased width of the depletion layer also decreases. this increases the width of the conducting channel and hence source to drain current OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS OF JFET The curve between drain current (Id) and drain source voltage (Vds)of a JFET at constant gate source voltage (VGS) is known as output characteristics of JFET .keeping Vgs fixed at some value 1 V the drain source voltage in steps. Corresponding to each value of Vds the drain current Id is noted. A plot of these values gives the output characteristics of JFET at Vgs = 1V repeating similar procedure output charaecteristics at other gate –source voltages . At first the drain current Id rises rapidly with drain surce voltage Vds but then becomes constant. The drain source voltage above which drain current becomes constant is known as pinch of f voltage.OA is the pinch off voltage. Shorted gate drain current (Idss) It is the drain current with source short circuited to gate Vgs =0 and drain voltage Vds equal to pinch pff voltage.it is called zero bias current. The drain current raise rapidly at first and then levels off at pinch off voltageVp. The drain current has now reached the maximum value Idss when Vds is incresed beyond Vp the depletion layers expand at the top of the channel.the channel now acts as current limiter and holds drain current constant at Idss Pinch off voltage Vp It is the minimum drain source voltage at which the drain current essentially becomes constant Gate – source cut off voltage Vgs (off) It is the gata source voltage where the channel is completely cut off and the drain current becomes zero. Expression for Drain Curent The relation between Idss and Vp .We note that gate – source cut off voltage VGS off on the transfer characteristics is equal to pinch off voltage vp on the drain characteristics Vp = VGS (off) JFET has VGS = -4 V Vp =4 ID= Idss (1-VGS/VGS(off))2 Id =drain current at given Vgs Idss = shorted -gate drain voltage Vgs = gate – source voltage Vgs (off) = gate –source cut off voltage FET AS A VOLTAGE –VARIABLE RESISTOR (VVR): FET is operated in the constant current portion of its output characteristics for the linear applications .In the region before pinch off , where Vds is small the drain to source resistance rd can be controlled by the bias voltage Vgs.The FET is useful as a voltage variable resistor (VVR) or Voltage Dependent resistor. In JFET the drain source conductance gd = Id/Vds for small values of Vds which may be expressed as gd = gdo [ 1-( VgsVp)1/2 ] where gdo is the value of drain conductance when the bias voltage Vgs is zero. The variation of the rd with vgs can be closely approximated by rd = ro / 1- KVgs ro – drain resistance at zero gate bias and K constant dependent upon FET type. Small signal FET drain resistance rd varies with applied gate voltage Vgs and FET act like a VARIABLE PASSIVE RESISTOR. Advantagesof JFET Very high input impedance order of 100 ohm Operation of JFET depends on the bulk material current carriers that do not cross junctions Negative temperature coefficients Very high power gain Smaller size longer life and high efficiency Ac drain resistance rd it is the ratio of change in drain – source voltage to the change in drain current at constant gate source voltage Transconductance it is the ratio of change in drain current to the change in gate source voltageat constant drain source voltage Amplification factor it is the ratio of change in drain source voltage to the change in gate source voltage at constant drain current. METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (MOSFET) The input impedance of a mosfet is much more than that of a JFET because of very small gate leakage current. The MOSFET can be used in any of the circuits converted for the JFET. CONSTRUCTION N – CHANNEL JFET There is only a single p region this region is called substrate A thin layer of metal oxide is deposited over the left side of the channel. A metallic gate is deposited over the oxide layer . Asilicon dioxide is an insulator ther fore gate is insulated from the channel .it is called Insulated Gate FET Like JFET , MOSFET has three terminals SOURCE, GATE, DRAIN. Working principle Instead of gate diode as in JFET here gate is formed as a small capacitor. One plate of the capacitor is the gate and the other plate is channel with metal oxide as the dielectric. when negative voltage is applied to the gate electrodes accumulate it. These electrons repel the conduction band electrons in the n channel. lesser number of conduction electron made available for current conduction through the channel. The grater the negative voltage on the gate the lessor is current conduction from source to drain. If the gate is given positive voltage more electrons are made available in the n channel.