* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
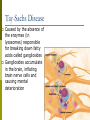
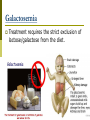
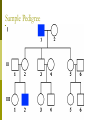
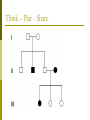
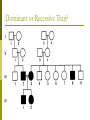
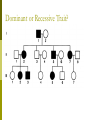
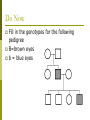
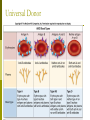
Albinism Caused by altered genes, resulting in the absence of the skin pigment melanin in hair and eyes White hair Very pale skin Blue Eyes Pink pupils Albinism Impaired Vision It is vital that people with albinism use sunscreen when exposed to sunlight to prevent premature skin aging or skin cancer High risk of skin cancer Tay-Sachs Disease Caused by the absence of the enzymes (in lysosomes) responsible for breaking down fatty acids called gangliosides Gangliosides accumulate in the brain, inflating brain nerve cells and causing mental deterioration Tay Sachs Disease Children with Tay-Sachs, a progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells, usually die before age 5. Children will go deaf, have seizures, and, ultimately, become unable to swallow or breathe. Galactosemia Recessive genetic disorder characterized by the inability of the body to digest galactose. Lactose = Galactose + Glucose Symptoms: • liver damage or failure • cataracts • brain damage • infection Galactosemia Treatment requires the strict exclusion of lactose/galactose from the diet. Dominant Genetic Disorders Dominant Gene results in disorder: Huntington’s Disease Achondroplasia Achondroplasia is a genetic condition that causes small body size and limbs that are comparatively short. Obesity Breathing problems (apnea) Recurrent ear infections (otitis media). Other health problems Huntington’s Disease affects the nervous system. Huntington's disease is a progressive, degenerative disease that causes certain nerve cells in your brain to waste away. As a result, you may experience uncontrolled movements, emotional disturbances and mental deterioration. Huntington’s Disease Diminished memory, immediate and shortterm (long-term memory usually remains intact) Disease usually manifests itself by age 35 Do Now Peter and Lois decide to try for a 4th child. Determine the possible genotype and phenotype ratios of the following cross: DdEe X ddEe D= Brown hair d=red hair E=fluffy hair e=thinning hair Pedigree Shows history of a trait in a family Allows researchers to analyze traits within a family Symbols for Pedigree Using Pedigrees Inferring Genotypes Knowing physical traits can determine what genes an individual is most likely to have. Predicting Disorders Scientists use pedigree analysis to study: inheritance patterns determine phenotypes genotypes. Sample Pedigree Think – Pair - Share Dominant or Recessive Trait? Dominant or Recessive Trait? Do Now Fill in the genotypes for the following pedigree B=brown eyes b = blue eyes Test Cross When the genotype of an individual is unknown, cross the individual with a homozygous recessive The outcome of the cross determine the genotype of the unknown Do Now Fill in the pedigree for Achondroplasia. Use the variable A. 11.2 Incomplete Dominance: Heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate phenotype between the two homozygous phenotypes. Two alleles are blended Ex) Four O’clock Flowers Red + White = Pink Codominance Neither trait is dominant instead, both traits are shown (No Blending) Ex) Roan Cows Red + White = RED AND WHITE Sickle Cell Disease Affects red blood cells and ability to transport oxygen. Homozygous recessive alleles= Heterozygous= Homozygous dominant alleles= Sickle Cell and Malaria People who are heterozygous for sickle cell, have a higher resistance to malaria. Multiple Alleles Traits determined by more than 2 alleles Ex. Blood Typing (3 alleles ABO) A and B are dominant to O Do Now A parent with the blood type A and one with B have a child with type O blood. What are the parents genotypes? Draw out the punnett square. Universal Donor Sample Problem Determine the possible offspring of the following crosses 1. AB and O 2. AA and BO 3. AB and AB Coat Color of Rabbits Rabbits have a hierarchy of coat color 4 alleles (C, cch, ch, and c) Dominant C > cch> ch > c Recessive C Full color cch Chinchilla ch Himalayan c albino Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity Coat Color of Rabbits Chinchilla Albino Full Color Himalayan Let’s try a sample problem cc x Ccch Genotype and phenotype ratios What do you see? What do you see? Sex Linked Traits Traits located on the sex chromosomes (X or Y) X linked: gene is located on the X chromosomes Y linked: gene is located on the Y chromosome What are the chances of having a girl? How would you go about solving it? Sex-Linked Traits A man who is color blind marries a woman that is heterozygous for color blindness. What is the chance of having a color blind boy? Do Now A man that is color blind marries a woman that is a carrier for the disorder. What is the chance of having a color blind girl? Hemophilia Sex linked disorder characterized by delayed blood clotting Located on the X Chromosome Seen in the Royal Family of England Hemophilia Chapter 11 Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity Polygenic Traits Polygenic traits arise from the interaction of multiple pairs of genes. Polygenic Inheritance P Generation aabbcc (very light) Skin Pigment AABBCC (very dark) F1 Generation AaBbCc AaBbCc F2 Generation Eggs Sperm Figure 9.22 What is the difference between polygenetic and multiple alleles? Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity Environmental Influences Environmental factors Diet and exercise Sunlight and water Temperature Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity Twin Studies Helps scientists separate genetic contributions from environmental contributions Traits that appear frequently in identical twins are at least partially controlled by heredity. Traits expressed differently in identical twins are strongly influenced by environment. Let’s try to explain the inheritance of the babies’ skin color. Chromosomal Mutations