* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
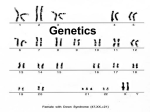
TAKS Objective 2 Day 3 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the organization of living systems. Genetics Genetics is the study of heredity. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are composed of DNA. Pieces of chromosomes are known as genes. You received one set of chromosomes from your mother (23) and one set from your father (23), totaling 46 chromosomes. Egg (from your mother) Sperm (from your father) Genes exist in alternative forms called alleles. Alleles are located on chromosome pairs. Gene for earlobe (attached) Gene for earlobe (unattached) Chromosome from mother Chromosome from father Gregor Mendel • It was not until the mid-nineteenth century that Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, carried out important studies of heredity— the passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring. • Characteristics that are inherited are called traits. Pea Plants • Mendel chose to use the garden pea in his experiments. Traits are passed from parents to offspring through units of information or genes. For each trait, an individual has two factors (alleles): one from its mother and one from its father. RR Rr homozygous heterozygous If the factors are the same from both, you are said to be homozygous for that trait. If the factors are different, you are said to be heterozygous. Each copy of a factor or gene is called an allele. A dominant gene will override or mask the recessive gene. • An uppercase letter is used for the dominant allele and a lowercase letter for the recessive allele. • The dominant allele is always written first. Short plant Tall plant T T t T t t F1 All tall plants T t The physical appearance, phenotype, of an individual is determined by the allele that codes for that trait. The set of alleles that an individual has is called a genotype. What the genes say….. A Punnett square is used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Punnett Squares (Monohybrid) Heterozygous & Heterozygous D d Heterozygous & Homozygous Recessive d d D Dd Dd D DD Dd d dd dd d Dd dd D d D D DD Dd Dd Dd D D DD Dd Homozygous Dominant & Heterozygous d d Dd Dd Homozygous Recessive & Homozygous Dominant Dihybrid crosses allow us to see when two traits from each parent is being utilized. AABB AABb AaBB AaBb AABb AAbb AaBb Aabb AaBB AaBb aaBB aaBb AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb Pedigree shows the Family Tree male female If the shapes are colored in, the individual is affected by the condition. Incomplete dominance is when two genes blend and produce a third phenotype. Red flowers mate with white flowers to produce pink flowers. Codominance occurs when both alleles are expressed. Roan cattle are codominant. When traits are controlled by more than two alleles in a population, it is said to be controlled by multiple alleles. Human blood type is controlled by three different alleles. In humans, there are four blood types (phenotypes): A, B, AB, and O. Blood type is controlled by three alleles, A, B, and O. A karyotype is a map of an organism’s chromosomes. Humans normally have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Chromosomes occur in pairs. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are sex chromosomes. They determine the sex of the individual. Females – XX Males - XY If an individual is missing or has too many chromosomes, a karyotype can be used. Trisomy – 3 chromosomes instead of 2 Monosomy – 1 chromosome instead of 2 An extra 21st chromosome is called trisomy 21 or Down’s Syndrome. A mutation is any change in the DNA of a cell. Mutations can be caused by: 1. Mistakes in replication 2. Mistakes in transcription 3. External agents A mutation can only be passed to offspring if it occurs in the gamete. Occasionally, a genetic mutation can be beneficial (helpful) to an organism. The peppered moth experienced a beneficial mutation which allowed it to camouflage itself to hide from predators. Question 1 Any change in DNA sequences is called a _______. A. replication B. mutation C. transcription D. translation The answer is B. Learning Check #2 What is a mutation? A change in the DNA sequence 3. Answer: A Allele Low-yield High-yield Rapidly maturing Slow-growing Tall Short Yellow kernels White kernels Symbol H h M m T t Y y Answer: A 4. An agricultural scientist wants to develop a variety of corn that will mature rapidly and will produce high yields. Which genotypes should the scientist cross to produce the most plants with the desired characteristics? A hhmmTtyy × hhMMttyy B HHmmttyy × hhMMttyy C hhMmttyy × HhmmttYY D HHmmttyy × hhMmttYy #5 The combination of alleles inherited is called the genotype . #6 The expression of traits is called the phenotype . #7 If an individual inherits one dominant allele and one recessive allele, the genotype is heterozygous . Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of naming and classifying organisms. Classifying Organisms by name • Binomial Nomenclature – naming organisms using a two-part name. –First word is the Genus (always capitalized) –Second word is the Species (lower case) Example: Homo sapiens – Homo is the genus name. – sapiens is the species name. The scientific name of an organism should always be italicized or underlined. Classifications • Kingdom Largest • Phylum • Class • Order • Family • Genus • Species Smallest • • • • • • • King Phillip Came Over From Greece Sneezing Learning Check #1 Which is the largest classification of organisms? A. Species B. Genus C. Family D. Order D #2 Which is the most specific classification? A. Species B. Genus C. Family D. Order A 6 Kingdoms • • • • • • Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Archaebacteria • Includes only prokaryotes • Archaebacteria live without oxygen; in extreme habitats (salt lakes, swamps, deep ocean thermal vents, hot springs) Eubacteria • They too are prokaryotic, meaning they have no membrane-bound nucleus. • Some use cilia or flagella to help them move. Bacteria are classified according to their shape. Cocci – round Bacilli – rod shaped Spirillum – spiral shaped Eubacteria can cause disease Diseases caused by Eubacteria include: – Tetanus, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, strep throat, and staph infections. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections. Antibiotics are useless against viruses! The spread of harmful bacteria can be avoided by: 1. Washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water. 2. Covering your mouth and nose when sneezing and/or coughing. 3. Limiting the number of times you touch your face, mouth, eyes, and nose. 4. Cooking foods properly. Most Eubacteria do not cause infection or disease. Some bacteria are helpful by: 1. Aiding in the digestion process 2. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria helping plant roots grow Yogurt and swiss cheese are made with the help of bacteria. Bacteria are decomposers. Decomposers help break down dead and decaying matter. Learning Check #1 How are bacteria classified? According to their shape #2 An organism is single celled, does not have a nucleus, and lives in a deep sea thermal vent. What kingdom does it most likely belong to? A. Plantae B. Archaebacteria C. Eubacteria D. Animalia B Learning Check #3 A prokaryotic cell is found that causes diptheria. What kingdom would this organism belong to? A. Plantae B. Archaebacteria C. Eubacteria D. Animalia C #4 How would you classify a bacteria that was rod-shaped? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilli B Kingdom Protista • Eukaryotic • Unicellular & Multicellular • Most diverse group of all the kingdoms • Found mainly in moist environments • Ex: amoebas Protists are eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and other cell organelles. Kingdom Fungi • • • • Eukaryotic Most are multicellular Many are decomposers Ex: mushrooms, yeast, & mold Kingdom Plantae • Multicellular Eukaryotes • Stationary (cannot move around) • Have cell walls made of cellulose. Plants are autotrophs. Plants can make their own food by way of photosynthesis. Plants have chloroplasts in their cells, which allow the plant to convert the energy from sunlight into chemical energy for the plant. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. What is required for photosynthesis to take place? 1. Sunlight 2. Water 3. Carbon Dioxide Kingdom Animalia • Multicellular Eukaryotes • Consumers or Heterotrophs • Mobile – can move from place to place • No cell walls • Have tissues that are organized into organs and organ systems Animal cells do not have cell walls. Learning Check #1 A scientist discovers a multicellular eukaryotic organism that moves to obtain food. What kingdom does it most likely belong to? A. Plantae B. Archaebacteria C. Eubacteria D. Animalia D 2. A group of scientists discover a new species in a rain forest. They take a tissue sample from one of the organisms and look at it under a microscope. The cells making up the tissue have nuclei and cell walls. Next the scientists take several of the organisms and place them in damp soil that is rich in organic material. Half of the organisms are exposed to full sunlight, and half are kept in constant darkness. The group that receives sunlight grows and thrives, but the group that is kept in darkness gradually dies. In which kingdom should the new species be classified? A Eubacteria B Fungi C Plantae D Animalia Answer: C 3. Which of these classifications is most specific? A Family B Genus C Phylum D Order Answer: B 4. Some bacteria benefit mammals by helping with• — Kingdom Bacteria has F growth G defense H digestion J respiration beneficial and harmful members • The best answer here is H, since digestion systems of mammals contain bacteria. • Bacteria found in the respiratory system usually result in illness, which would trigger the defenses, not help them. 5. The bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis produce protein crystals that are toxic to the digestive system of insects. How can these bacteria be used to control insects in crops? F G H J Apply the bacteria to growing plants. Expose the bacteria to low levels of light. Remove plants from areas containing the bacteria Treat the bacteria with a solution of the protein crystals Answer: F 6. The bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, is most closely related to the — F spotted chorus frog, Pseudacris clarki G Asian flying frog, Polypedates leucomystax H northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens J African bullfrog, Pyxicephalus adspersus Related in biological terms means family, genus, species. F spotted chorus frog, Pseudacris clarki G Asian flying frog, Polypedates leucomystax H northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens J African bullfrog, Pyxicephalus adspersus • Genus is always a capital letter, species is lower case. • Most closely related would be in the same genus, Rana. • ANSWER? • H C TAK Obj. 02 TEKS B.8C