* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendel`s Work
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
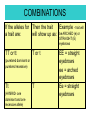
Mendel’s Work What is Heredity? • The passing on of characteristics (traits) from parents to offspring • Genetics is the study of heredity • Some examples of traits are: eye color, height, nose shape, etc! • Monk from Austria in mid-1800’s • Cross-pollinated pea plants to see what traits were inherited by following generations • Importance of his experiments not recognized until 1900’s • Now known as Father of Genetics Steps of Mendel's Experiment Mendel crossed them • Gametes- male and female sex cells • Fertilization - the uniting of male and female gametes • Cross - combining gametes from parents with different traits Each organism has two ALLELES for each TRAIT • Alleles - different forms of the same gene • Genes - located on chromosomes, they control how an organism develops • Purebred - offspring of many generations with the same trait (both alleles the SAME) Mendel’s Experiment • P (parent) generation- He first crossed two purebred pea plants – one that had two alleles for being TALL, one that had two alleles for being SHORT • F1 (first filial) offspring- They were ALL TALL!!!! • F2 (second filial) offspring- About ¼ of this generation were SHORT! Rule of Dominance • The trait that is observed in the offspring is the dominant trait (uppercase) • The trait that disappears in the offspring is the recessive trait (lowercase) COMBINATIONS If the alleles for Then the trait Example - trait will a trait are: will show up as: be ARCHED (e) or STRAIGHT (E) eyebrows TT or tt T or t (purebred dominant or purebred recessive) Tt (HYBRID- one dominant and one recessive allele) T EE = straight eyebrows ee = arched eyebrows Ee = straight eyebrows