* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lum, 2004
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
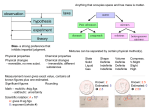
Discovering Modes of Action for Therapeutic Compounds Using a Genome-Wide Screen of Yeast Heterozygotes Pek Yee Lum, Christopher D. Armour, Daniel D. Shoemaker, et al. Cell, Vol. 116, 121-137, January 9, 2004 Purpose of this paper: Knowledge of the underlying molecular mechanisms of drugs + their targets Use of “Fitness Profiling” for understanding drug activities INTRODUCTION Need for new tools that can rapidly identify protein targets of small molecules. i.e. Protein arrays, reverse transfection, and DNA microarrays Saccharomyces cerevisiae APPROACH A study by Giaever et al. (1999) demonstrated that parallel analysis of yeast strains with heterozygous deletions of drug target genes can be used to monitor compound activities in vivo. reducing the gene copy number of drug targets in a diploid cell can result in sensitization to the drug of interest. NOW……in this paper: They extended this approach to analyze the activities of 78 chemical entities, most of which are medically relevant. Increased the number of mutant strains…why?? Used high-density oligonucleotide arrays with a two-color labelling strategy…..to do what ?? Finally, a strain-specific error model was used….to do what ?? In this study, they correctly identified the reported targets for many well-characterized compounds in addition to discovering many potentially novel drug targets. Result #1: Study Design Rationale Figure 1. Schematic Representation of the Fitness Profiling Experimental Strategy RESULT #2: Identifying Drug-Specific Growth Defects Result #3: Large-Scale Analysis of 78 Compounds Figure 3. Comprehensive View of Fitness Profiles for 78 Compounds Result #4: Inhibition of Lanosterol Synthase (Erg7p) by Molsidomine Result #5: Disruption of Exosome-Specific rRNA Processing by 5-Fluorouracil Result #5….continued Discussion Use of Fitness Profiling for Understanding Drug Activities Advantages: Requires no prior knowledge of compound mode of action, which allows truly novel drug activities to be uncovered in a systematic and unbiased fashion Biological processes that are affected by a given compound are identified in addition to the precise protein target(s) Limitations and Technical Considerations: The compound of interest must be able to affect the growth rate of the cell. However, the ability of a compound to affect the growth rate of yeast does not guarantee that a target will be identified by this approach. The activity level of the targeted protein must be influenced by the dosage level of the corresponding gene under the conditions profiled. Finally, compounds that exert their effects through direct interaction with nonprotein elements in the cell, such as DNA or ergosterol, do not appear suitable for this approach.