* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download catalyst
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
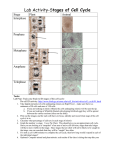
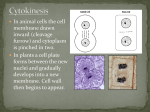
CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 8:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 7:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 6:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 5:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 4:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 3:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 2:00 MINUTES The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST TIME REMAINING: 1:00 MINUTE The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What is the difference between a trait, gene, and an allele? What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? CATALYST Silently and on your own, complete the task below When you are finished, put your pencil down and look up. Remain silent to allow others to finish. 2. Brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b). A father has brown eyes. Which of the following could be the father’s genotype? A. BB B. Bb TIME REMAINING: 2:00 MINUTES C. bb D. BB and Bb 3. The products of anaerobic respiration include... A. sugar B. oxygen C. carbon dioxide D. lactic acid only CATALYST Silently and on your own, complete the task below When you are finished, put your pencil down and look up. Remain silent to allow others to finish. 2. Brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b). A father has brown eyes. Which of the following could be the father’s genotype? A. BB B. Bb TIME REMAINING: 1:00 MINUTES C. bb D. BB and Bb 3. The products of anaerobic respiration include... A. sugar B. oxygen C. carbon dioxide D. lactic acid only CATALYST The CATALYST is to be done independently and silently. Answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What sort of images and words do you associated with the term “genetics?” Provide a list with appropriate explanations. CATALYST Silently and on your own, complete the task below When you are finished, put your pencil down and look up. Remain silent to allow others to finish. 2. Brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b). A father has brown eyes. Which of the following could be the father’s genotype? A. BB B. Bb C. bb D. BB and Bb 3. The products of anaerobic respiration include... A. sugar B. oxygen C. carbon dioxide D. lactic acid only HOMEWORK 1. Formative Friday 2. Vocabulary Assessment CANCELLED (due to Summative) SUMMATIVE SCORES • Data Tracking scheduled after formative assessment (Friday) MITOSIS • There are about 50 trillion cells in the human body • If you get an injury, you lose cells How can you grow more cells? Mitosis = a cell divides in half to make 2 identical cells (2 clones) daughter cell Parent cell MITOSIS In mitosis, a cell divides 1 time; 1 cell division occurs The cells produced by mitosis are identical to the parent cell daughter cell Parent cell Why do our cells undergo or “do” mitosis? • Cells do mitosis to help our bodies grow and repair themselves • Unicellular organisms (1 cell--like bacteria) do mitosis to reproduce • Asexual reproduction: reproduction with 1 parent Mitosis (notes) • Mitosis happens in 4 stages • Chromosome: strand of DNA Mitosis (notes) Stage 0: Interphase Before mitosis starts Description: Genetic material is loose (not formed in chromosomes) the cell is preparing for cell division the cell obtains nutrients, grows, and conducts its “normal” functions Mitosis (notes) Stage 1: Prophase Description: chromosomes form chromosomes condense Mitosis (notes) Stage 2: Metaphase Description: • Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell • Each chromosome connects to a spindle Mitosis (notes) Stage 3: Anaphase Description: Chromosomes split and spindles pull them to opposite ends of the cell Mitosis (notes) Stage 4: Telophase Description: Chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell Mitosis “Stage 5”: Cytokinesis Description: Separation of cytoplasm resulting in two distinct daughter cells Exit Ticket • If a cell undergoes mitosis, are the daughter cells the same or different from each other? • Is mitosis a form of sexual or asexual reproduction • What is a chromosome? • What is the mnemonic (memory aid) for mitosis? • What are the 5 stages of mitosis? • Describe the major characteristics of metaphase.