* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GMO—Detecting Genetically Modified Foods
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Monsanto Canada Inc v Schmeiser wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food in Hawaii wikipedia , lookup
Mendocino County GMO Ban wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
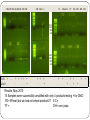
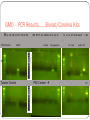
GMO—Detecting Genetically Modified Foods Testing Foods for Introduced Genes GMO’s • Genetically modified organisms have DNA that has been modified through genetic engineering • GM foods were first put on the market in the early 1990s fueling a revolution in agriculture For plants…the gene may come from another plant, or from another species, or from another kingdom. Introduced DNA codes for a protein that gives the GMO an advantage over the wild type GMO-Animals Animal products have been proposed or produced ▫ Pig engineered to produce omega-3 fatty acids. ▫ Sheep that express antibodies in milk GMO’s - Plants Genetically modified plant products: soybean, corn, canola, and cotton seed oil. Genes encode herbicide resistance, insect resistance, drought tolerance, frost tolerance, delayed fruit ripening and other traits. GMO Plants Flavr Savr tomato the first commercially grown genetically engineered food granted a license for human consumption Produced by the Californian company Calgene 1992 Sold in 1994, and was only available for a few years before production ceased Flavor-sav Vs Normal More resistant to rotting and softening by adding an antisense gene which interferes with the production of the enzyme polygalacturonase (see RNA interference). Softening makes the tomato more susceptible to being damaged by fungal infections. Wide Variety of Tomatoes Picked BEFORE they are ripe….still very firm Artificially ripen with ethylene gas Easier handling and shelf life BT-Corn Bt corn is a variant of maize, genetically altered to express the bacterial Bt toxin Poisonous to insect pests. In the case of corn, the pest is the European Corn Borer BT-Corn A gene from a microorganism Bacillus thuringiensis inserted into the corn genome. The gene codes for a protein toxin that forms a crystalline product…the product is eaten & perforates the larval digestive tract. The pores allow naturally occurring enteric bacteria such as E. coli and Enterobacter to infect the insect causing death Round-up Ready Roundup is the brand name of a systemic, broadspectrum herbicide Produced by Monsanto The active ingredient glyphosate Round up Ready Monsanto also produces seeds which grow into plants genetically engineered to be tolerant to glyphosate which are known as Roundup Ready crops. The genes contained in these seeds are patented. Roundup Ready Crops In 1996, genetically modified Roundup Ready soybeans resistant to Roundup became commercially available, followed by Roundup Ready corn in 1998 Current Roundup Ready crops include soy, maize (corn), canola, sugar beet, and cotton, with wheat, and alfalfa still under development. No Till Farming Using Round-Up eliminates ALL plants…except those that are genetically modified No need to till (plow-turn over) the fields. Preserves the top soil “But plow-based farming in this region cultivated an unexpected yield: the loss of fertile topsoil that literally blew away in the winds” Glyphosate Resistance Found! The C4 strain of Agrobacterium A species of bacteria that was found growing in the wastefed column at a factory that made glyphosate. The EPSP synthase enzyme from this bacterium (C4 EPSP synthase) was almost completely insensitive to glyphosate Agrobacterium tumefaciens This bacterium infects plants and injects DNA from a plasmid into plant cells Injected DNA enters the nucleus and becomes incorporated into the plant chromsomes. Under normal circumstances Agrobacterium tumefaciens causes gall tumors in plants Roundup Ready Cloning The C4 EPSP bacterial gene was cloned and inserted into a bacterial plant vector in order to prepare for cloning into plants. The Monsanto C4 EPSP cloning vectors first patented September 13, 1994 Roundup Ready Cloning A plasmid vector that will work in E. coli Needs also characteristics that allow the plasmid to work in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Needs a promoter…..to turn on the gene in plants! Roundup Ready Cloning A plant promoter (P-35S) is 35S inserted at the 5' end. This promoter is the 35S promoter from cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV). The 3' end of the gene is modified by inserting the polyadenylation site (NOS 3') from the nopaline synthase gene of the tumorinducing (Ti) plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. 5’ Resistance aaaaaaaaaaa 3’ Roundup Ready Transformation Agrobacterium tumefaciens. infects plants and injects DNA into plant cells where it enters the nucleus and becomes incorporated into the plant chromsomes. The recombinat DNA is transferred and no tumors are formed. Roundup Ready Roundup Ready soybean was the first crop plant produced by Monsanto. Today, 90% of the soybean crop in the USA consists of Roundup Ready® plants. You can't buy soybean products that don't come from genetically modified plants. How to make a Genetically Modified Plant Isolate gene that direct cells to make protein of interest (From bacteria in the sewers of the chemical plant making RR) Attach the gene to the promoter that works in plant (Califlower mosaic virus 35S) Insert the promoter-gene and a gene for selectable marker into plant cells Agrobacterium tumefaciens Allow the genetically altered cells to grow into plants. Detection technology of GMOs Real-time PCR DNA Microarray Captured PCR-ELISA Quicktest strip How to Detect a GMO Isolate DNA from plant tissue and food products. (PCR) is used to assay for evidence of the 35S promoter that drives expression of the glyphosate resistance gene and many other plant transgenes. Real-time PCR Screening Kits Target genes: CaMV 35S Promotor, Nos teminator , NptII, Bar, FMV promotor, Pat Reference gene: 18S rRNA Quantitative Kits Roundup Ready soybean Bt176 Maize Event-specific detection kits GTS40-3-2, Bt176, Mon810, Bt11, GA21, T25, RT73 35S PROMOTER INDICATES GMO Herbicide resistance correlates with an insertion allele – the 35S promoter – that is readily identified by electrophoresis on an agarose mini-gel. Amplification of tubulin, a protein found in all plants, provides evidence of amplifiable DNA in the preparation, while tissue from wild-type and Roundup Ready® soy plants are positive controls for the 35S promoter. Two PCR reactions are performed for each plant or food sample. One primer set amplifies the 35S promoter from cauliflower mosaic virus. The presence of a 35S product is diagnostic for the presence of a transgene. The 35S promoter is used to drive expression of the glyphosate (Roundup) resistance gene or Bt gene in edible crops. A second primer set amplifies a fragment of a tubulin gene and controls for the presence of plant template DNA. Since the tubulin gene is found in all plant genomes, the presence of a tubulin product indicates amplifiable DNA in the sample isolated. Tubulin is a housekeeping gene Results of a GMO Test PCR to Detect GMO The following primer sets were used in the experiment: 5'-CCGACAGTGGTCCCAAAGATGGAC-3' (Forward Primer) 5'-ATATAGAGGAAGGGTCTTGCGAAGG-3' (Reverse Primer) 5'-GGGATCCACTTCATGCTTTCGTCC-3' (Forward Primer) 5'-GGGAACCACATCACCACGGTACAT-3' (Reverse Primer) PCR Characteristics Denaturing step: 94 C 30’ Annealing step: Extending step: 60 C 30” 72 C 30’ 34X.. 35S ----162 base pairs Tubulin-187 base pairs RG DP BS AS EC AS KR FD CB AM + c TL ASca TJ TF SC DH DH DH 2000 1600 1000 500 2000 1600 1000 500 PCR + - GMO - + + + + + - - - - + + + + - - + + - + - - + + + - + + + - Results: May 2010 15 Samples were successfully amplified with only 4 products testing + for GMO FD= Wheat (but we had not wheat products?? S C= TF = DH= corn pops + - GMO – PCR Results…….Biorad/Carolina Kits M SL AB NB CW CT RH LB RB S35 Promoter CHIPS WM RP TS AH HB EB CV AL AK M Cracker Veg. pepperoni M LH NF BF TW MH SB ZP Tor. Chip + MM pretzel PC 500 Tubulin Control PSII Control PC Results: 14 Food items were tested for genetic modification using the S35 promoter from CMV as a marker Tubulin or Photosystem II used for a negative control 9 samples had + PCR results 5 samples showed +results for the S35 promoter Problem cracker and tortilla chip PCR product wrong size. Chips and pretzel don’t have + controls Conclusions: Tortilla chips, pretzels, veggie pepperoni and club crackers appear to contain food from GMO’s Wrong size products, no tubulin make conclusion regarding pretzel and cracker suspect Surprize—wheat products have generally not been reported to contain this genetic modification. Perhaps they also contain corn or soy products. Further testing would be necessary to confirm. Need to optimize the procedure.