* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
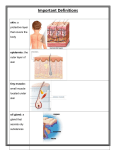
By Jittipan Chavadej , Ph.D. , yr. 2000 Anatomy Dept.,Fac. of Science Structural development •begin as a single layer of ectodermal cells •formation of a thin outer layer periderm at the end of the first month •third month- three layers - basal layer, intermediate layer&supl layer of peridermal cells Diagram showing the formation of the skin at various stages of development •6th month -epidermis beneath periderm differentiation into the definitive layers •Sloughs of peridermal cells into the amniotic fluid •Immigrant cells in the epidermis -2nd month -melanoblast -late in 1st trimester -Langerhans cells -Merkel cells Melanoblast (-cyte) : -derived from neural crest -midpregnancy-begin producing pigment granules = melanosomes Dark skin-more pigment granules/cell Albinism -genetic trait, lack of enzyme-tyrosinase:tyrosine melanin Epidermal differentiation Movement of epidermal cells - loss of adhesiveness e.g. fibronectin, laminin&collagen types I&IV Keratohyalin granules (histidine&sulphur- rich), (closely associated with keratin filament)- stratum granulosum (keratinocyte) Keratin filaments-stratum corneum Lost nuclei -bag of densely packed with keratin filaments •15-20 layers of dead cells Flattened cell-breaking up nuclear membrane Produce keratin filament (desmosome) Unspecialized cells - mitotic activity One of the prominent features of thick skin=presence of epidermal ridges and creases ->loops & whorls Dermatoglyphics-basic patterns(epi. ridge) for genetic analysis or criminal investigation (unique to individual) Dermis •Mesodermal cells from dermatome / beneath ectoderm •3rd month -transition from highly cellular embryonic form fibroblast + fibrous intercellular matrix •Becomes highly vascularized + sensory nerve Future dermis-loosely aggregated mesenchymal cells Epidermal appendages Hair -induction from dermis -12th week :down growth of hair bud -hair papillae hair shaft epithelial hair sheath -arrector pili muscle :dermal root sheath & dermal papilla -sebaceous gl. fat-like substance hair follicle Diagram showing development of a hair and a sebaceous gland 5th mo. hair shaft-keratinization forming granules of trichohyalin(hardness of the hair) Late stage of hair formation-hair bulb--> melanocytes -->color Mammary Gland •Mammary line or ridge(6 wk.) :base of forearm region of hind limb Small solid outbudding lactiferous duct formation+alveoli of the gland epithelial pit (nipple-after birth) Diagram showing position of mammary line Stages in the embryonic development of the human mammary gland Abnormalities of Skin Development •Ichthyosis-genetically transmitted disorders of keratinization Harlequin -autosomal recessive disorder •Hypertrichosis- formation of hair follicle •Atrichia -congenital absence of hair A:milk line-mammary glands form along this line B:common sites of formation of supernumerary nipples/mammary gland •Polythelia - accessory nipples(axillary region) •Polymastia -supernumerary brests