* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
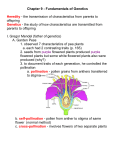
Why are peas useful for genetic studies? (What contributed to Mendel’s success? 1. Normally self-fertilize 2. One can manipulate the crosses (matings) by cutting off stamens (male part) and fertilizing the carpel (female part) with pollen from another plant. 3. Mendel used “true-breeding” varieties. Phenotypes What do we call each of these generations? Genotypes Purple flower X white flower P (parental) PP X pp Purple flowers (cross w. self) F-1 generation Pp X Pp Purple and white flowers F-2 generation PP, Pp, pP, and pp Which trait is dominate? purple What ratio of purple/ white flowered plants would you expect in the F2 generation? 3:1 Why? See genotypes What is the difference between a plant that homozygous versus heterozygous for a particular trait? In the homozygous plant the two alleles are identical. In the heterozygous plant the two alleles are different. Which is true-breeding? Homozygous Which is hybrid? Heterozygous Some definitions: What’s a phenotype? The expressed or physical traits. What’s a genotype? The genetic makeup leading to these traits. What’a an allele? An alternate form of a gene on the homologous chromosomes Mende l’s Hypo theses: As rephrased by C ampbe ll p158 1. There are alternative forms of genes, the units that determine heritable traits. 2. For each inhe rited characteristic, an organism has two genes, one from each parent. These genes may both be the same allele, or they may be different alleles. 3. A sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inhe rited trait, because allele pai rs separate (segregate) from each other during the production of gametes. 4. When the two gene s of a pair are different alleles and one is fully expressed while the other has no noticeable effect on the organism’s appe arance, the al leles are called the dominant allele and the recessive allele, respectively Variability and the Environment. Consider musical ability. Is it determined by genetics? By environment? Environmental influences can act at many levels. Gene expression can be affected by many variables including: Nutrients, toxins, hormones, even temperature. Some traits are determined entirely by the environment with no basis in the genome. Social traits that show the highest correlation between parent and offspring are politics and religion. Neither is genetically determined but is inherited if we simply measure correlation. Distinguish: Familial traits Shared by relatives for whatever reason. Heritable traits Shared by relatives because they have the same genes Which is easy to establish? Which is hard? It is hard to establish that a trait is heritable. What is the gen e that causes cystic fibrosis. ? Go to: http://genome.nhg ri.nih.gov/clone/ What are some diseases with simple dominant or recessive inheritance? Recessive disorders Albinism cystic fibrosis galactosemi a pheny lketonuria (PKU) sic kle-cell disease Tay- Sachs di sease Dominant disorders Achond roplasia Alzhe imer’s disease (One type ) Hun tington’ s dis ease Hype rcho lesterole mia (some types ) Fetal testing can spot many inherited disorders early in pregnancy. amniocentesis-- between 14th and 16th w eek, wit hdr aw some fluid through ne edle inserted through abdomen-- the test fluid wit hdrawn also has some cells . Grow cell s in cult ure and do a kayo type -- test for Down ’ syndro me (tris omy of chromosome 21); test for Tay s Sachs dis ease. 1% risk of compli cation. chorionic villus sampli ng (CVS) insert tube through vag ina into cervix and it no u terus and suc tion off a small amount of fetal ti ssue (cho rionic villi ) from placenta. The se cell s are rapidly grow ing and thu s allow a rapid test-- i.e. wit h in a few hour s. Second advan tage is that CVS can be per formed earli er--between 8th and 10 th week. 2% risk of compli cation. Ultra sound-- non- invasive, has no known risk. fetoscopy. Tube inserted like in CVS but carries a camera-- allows phys ician to look at growing fetus. 10% risk of complication. What determines which tests are used? Consider the inheritance of two traits at once. Round yellow peas RRYY Gametes: RY X wrinkled green peas rryy X ry Round yellow peas RrYy Gametes: RY, Ry, rY, ry X RY, Ry, rY, ry Round yellow, green round, yellow wrinkled, green wrinkled RRYY 1 rrYY 1 RRyy 1 RRYy 2 rryy 1 rrYy 2 Rryy 2 RrYY 2 RrYy 4 Total: 9 3 3 1 There are lots of different genotypes that could give a plant with the phenotype of round and yellow peas. If you had such a plant, how could you determine what genotype it had? Cross it against a double recessive plant, i.e. in this case a plant with green wrinkled peas. Parental? RRYY RRYy X ry RrYY RrYy F1 Genotypes RrYr RrYy and Rryy RrYr and rrYy RrYy, rrYy, Rryy, rryy F1 Phenotypes All round and yellow All round, both green and yellow All yellow, both round and wrinkled Both yellow and green, both round and wrinkled The rules of probability (statistics) can predict the outcome of a particular cross. If AaBb is crossed with AaBb, what is the probability of having an aa offspring? 1/2 X 1/2 = 1/4 What is the chance of having a bb offspring? 1/2 X 1/2 = 1/4 What is the chance of having either an aa or a bb offspring? 1/4 + 1/4 = 1/2 What is the chance of having an offspring with both aa and bb? 1/4 X 1/4 = 1/16 Rules of probability (Campbell p 162 ) 1. Probability scale is from 0 to 1. An event certain to occur has probability = 1 An event certain Not to occur has probability = 0 Consider a situation where the outcome of any p articular event is unaffected by what has happen ed on previous event s (i.e. for a coin toss, each toss the probability of getting a head is 1/2). Thu s each even t in an independent event. 2. The rule of multiplicity relates to the out come o f two independen t events (i.e. the toss of two coins). The probability of a compound event (i.e. getting t wo heads) is the product of separate probabilities of the independ ent event s (i.e. 1/2 X 1/2 = 1/4). A biological example is the probability of getting a r ecessive homozygote o ffspring from two heterozygo te parents. 3. The rule of addition relates to an event that could occu r in two or more alternative ways (i.e. the p robability of getting a head and a tail from the toss of two coins). The probability of such an event is the su m of the probabilities of the different ways. (1/4 + 1/4 = 1/2) A biolog ical example is the probability o f getting a hete rozygote offspring from two heterozygo te pa rents.